
Sustainable Supply Chains: Strategies for Environmental Responsibility and Social Impact
Dr. Prakash Divakaran
1![]() , Dr. Vandana Mishra Chaturvedi 2
, Dr. Vandana Mishra Chaturvedi 2![]()
1 Pro-Vice
Chancelor, & Professor, Department of Business Administration, Himalayan
University, Itanagar, Arunachal Pradesh, India
2 Vice-Chancellor,
D Y Patil Deemed to be University, Sector -7, Vidya Nagar, Nerul, Navi
Mumbai-400706, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Over the last
several years, there has been a significant uptick in the amount of focus
that has been placed on the idea of environmentally and socially responsible
supply chains as a consequence of the global rise in
awareness about issues of environmental and social impact. This study's
objective is to analyze the many strategies and methods that companies may
use in order to build supply chains that are
environmentally friendly and sustainable. The paper explores significant
topics such as social responsibility, ethical sourcing, and environmental
stewardship to highlight how vital it is to include ideas of sustainability
in supply chain management. The report also highlights how important it is to
integrate principles of sustainability into supply chain management. In
addition to this, the research looks at the many benefits that come with
sustainable supply chains, as well as the challenges that come with putting
them into action and the rising trends in this sector. The findings provide a
substantial addition to the body of knowledge around the management of
sustainable supply chains and give vital insights to businesses that are
seeking to align the operations of their supply chains with environmental and
social objectives. |
|||
|
Received 23 November 2023 Accepted 20 December 2023 Published 31 December 2023 Corresponding Author Dr.
Prakash Divakaran, prakash@himalayanuniversity.com DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v11.i12.2023.6252 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2023 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the license
CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download, reuse,
re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work must
be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Sustainable Supply Chains, Technological,
Digital Security and Privacy, Digital Environment, Technology Privacy |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
In today's interconnected world, sustainability is a crucial consideration across all industries. As new environmental and social concerns emerge, the management of sustainable supply chains is taking on an increasingly critical role. Sustainable supply chains encourage economic prosperity, environmental responsibility, and social impact. The management of sustainable supply chains can satisfy the growing demand for products and services that are both ethical and environmentally beneficial. Consumers, stakeholders, and regulators are increasingly concentrating their attention on the environmental and social policies and procedures that businesses implement. Businesses are under a lot of pressure to evaluate and make changes to their supplier networks so they can reach their sustainability goals.
This article explores the ways in which businesses might build supply networks that are environmentally friendly. It highlights areas for improvement such as environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and ethical sourcing while also emphasizing the necessity of sustainability in supply chain management. These concepts could assist businesses in enhancing their supply chains while simultaneously safeguarding the environment and society. Brandenburg et al. (2017) This paper will contain sections on environmentally responsible purchasing, energy efficiency, trash reduction, and reducing carbon footprints. Strategies for social effect will consist of labor norms and human rights, diversity and inclusion of suppliers, community engagement, and responsible sourcing. These methods assist companies in achieving sustainability and contributing to societal advancement. According to the findings of the study, sustainable supply chains include stakeholders, minimize risk, save money, boost brand image, and also save money. It will show the ethical and competitive advantages of integrating supply chain practices with sustainability objectives, as well as highlight the benefits of doing so. On the other hand, sustainable supply networks create challenges. This presentation will discuss the complexities of supply chain networks, including data collection and transparency, stakeholder alignment, and adapting to changing trends. Understanding and addressing these challenges is important for organizations that want to maintain sustainable and ethical supply chains. Rühmkorf (2015)
2. Objective
The research aimed to fulfill the following objectives:
· The Meaning of Sustainable Supply Chains and Why They Are So Important?
· Result and discussion
· The Importance of Being Responsible for the Environment and Having an Impact on Society
3. Methodology
An all-encompassing research examined sustainable supply networks' environmental and social implications. A thorough literature review collected sustainable supply chain data. Academic, business, and trustworthy publications were evaluated. This helped evaluate knowledge, identify trends, and learn about cutting-edge environmental sustainability and social change strategies.
Primary and secondary sources provided data. Researchers interviewed and surveyed supply chain professionals, sustainability experts, and industry practitioners to learn about sustainable supply chain projects. Academic papers, industry reports, and case studies backed the results and disputes. We assessed data using qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative analysis analyzed and classified the data using themes, patterns, and key environmental responsibility and social impact techniques. The quantitative examination of survey or industry report data was utilized to determine technique frequency and effectiveness. Case studies showed how organizations may implement sustainable supply chain strategies. These case studies illuminated environmental responsibility and social impact challenges, methods, and outcomes. The literature review, data analysis, and case studies produced a sustainable supply chain strategy framework. This approach simplified supply chain sustainability. This study employed a number of sources to gather knowledge, analyze current data, and provide a roadmap for firms to implement sustainable supply chain strategies. This study examined sustainable supply chain solutions for environmental and social effect using a rigorous methodology to verify credibility and value.
4. The Meaning of Sustainable Supply Chains and Why They Are So Important?
A sustainable supply chain is one that takes environmental, social, and economic factors into account throughout the process of designing, planning, and carrying out activities associated with supply chain operations. It entails adopting policies and practices that enhance social well-being, reduce negative consequences on the environment, and assure long-term economic viability.
The need to solve urgent problems on a global scale, such as climate change, the depletion of natural resources, social inequality, and ethical issues, is the driving force behind the need of establishing sustainable supply chains. Companies are aware that the operations of their supply chains may have substantial effects on the environment and on the communities they serve; as a result, they acknowledge that it is their obligation to manage these supply chains in a sustainable way. The following are some of the advantages that businesses may get if they integrate sustainable practices into their supply chains Aliyu (2019)
Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable supply chains contribute to the preservation of the environment by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, limiting waste output, preserving natural resources, and supporting the use of renewable energy. In addition, these practices help to minimize the amount of trash that is produced. This helps alleviate the negative environmental effect that activities throughout the supply chain have, and it facilitates the transition towards a world that is more sustainable and resilient.
Economies of Scale and Improved Productivity: Embracing environmentally friendly business practices often results in increased economies of scale and improved productivity. For instance, improving transportation routes may lower the amount of gasoline used as well as the cost of transportation, while waste reduction measures can reduce the amount of money spent on disposal and materials. Additionally, the costs of utilities may be cut by implementing energy-efficient processes and resource conservation initiatives.
Reputation of the Brand and Loyalty of Customers: Consumers are increasingly demanding that businesses show a commitment to sustainability in order to purchase goods and services from those businesses. The reputation of a company's brand is improved, trust is established with consumers, and customer loyalty is increased when the supply chain is environmentally responsible. Companies that distinguish themselves in the market by aligning their supply chains with environmental responsibility and social effect are more likely to attract customers who are ecologically and socially sensitive. Gaur and Vazquez-Brust (2019)
Risk Mitigation and Resilience: Sustainable supply networks are better suited to manage and reduce risks associated with environmental and social disturbances. Resilience is another benefit of sustainable supply chains. firms are able to design supply chains that are more resilient to disruptions caused by climate change, legislative changes, societal unrest, or supplier concerns if they take into consideration possible risks and implement preventive solutions. This allows the firms to be better prepared to manage such disruptions. Xu et al. (2019)
5. The Importance of Being Responsible for the Environment and Having an Impact on Society
The duty that companies have to reduce the amount of harm they do to the environment is what is meant by the term "environmental responsibility." It includes measures such as the management and reduction of carbon emissions, the conservation of resources, the adoption of activities that are sustainable, and the protection of ecosystems. When it comes to addressing climate change, lowering pollution levels, and preserving natural resources for future generations, environmental responsibility within supply chains is very essential. Liao (2023)
The term "social impact" refers to the consequences that company activities have on society as a whole, which includes the perspectives of many stakeholders such as workers, local communities, and society at large. It comprises supporting community development efforts, fostering diversity and inclusion, guaranteeing fair and safe working conditions, and protecting human rights along the whole supply chain. Initiatives with a social effect may help improve people's livelihoods, which in turn can improve their overall well-being and lessen social inequality.
The importance of social responsibility and environmental responsibility resides in the fact that they both contribute to the creation of a sustainable and equitable future. It is the obligation of businesses to evaluate not only how their activities affect the development of profits but also how those operations affect society and the environment as a whole. By incorporating environmental responsibility and social impact into their supply chains, businesses have the potential to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development objectives, increase the trust of their stakeholders, and generate a good reputation for themselves as responsible corporate citizens. In addition to this, it assists in the development of a society that is more open-minded, equal, and resilient. Rühmkorf (2015)
Figure 1
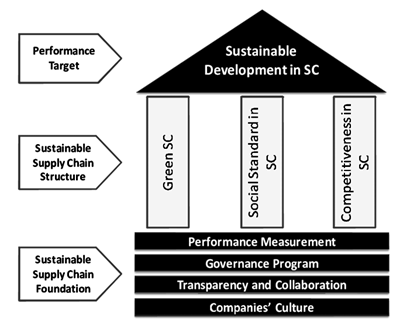
|
Figure 1 Sustainable Supply Chain |
6. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Strategies for Environmental Responsibility It is essential, for the purpose of minimizing negative effects on the environment, to put environmental responsibility strategies into practice throughout supply chains. According to the results, environmental sustainability may be achieved by enterprises via the implementation of a variety of techniques, such as green procurement, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and reduction of their carbon footprint. The practice of purchasing goods and services from companies that are conscious of their impact on the surrounding ecosystem is known as "green procurement." trash reduction techniques strive to decrease trash production and encourage circular economy activities. Energy efficiency measures concentrate on minimizing energy usage across the supply chain. Rodríguez‐González et al. (2022) Circular economy practices focus on reusing and recycling materials. Measurement and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions are included in carbon footprint reduction methods. These emissions may be cut by optimizing transportation, using sustainable packaging, and using alternative fuels.
The need of implementing social impact techniques in environmentally responsible supply chains is brought to light in the aforementioned research. Organizations may handle their social obligations by implementing methods such as maintaining labor standards and human rights, fostering supplier diversity and inclusion, participating in community development programs, and adopting responsible procurement. These are just few of the many possible solutions. Contributing to social well-being and sustainable development include activities such as promoting diversity, connecting with local communities, and establishing working conditions that are just, safe, and fair. Xu et al. (2018)
Advantages of Implementing Sustainable Supply Chain Practices The adoption of environmentally responsible supply chain practices results in a number of advantages. The findings suggest that firms might reduce their risk exposure by reducing the number of interruptions in their supply chains that are triggered by environmental or social concerns. It is possible to save costs by running operations more efficiently with regard to energy use, cutting down on waste, and improving logistics. In addition, companies that place an emphasis on sustainability may improve their brand image, which in turn helps them attract customers who are ecologically and socially sensitive and encourages stakeholder participation. These advantages help firms improve their long-term financial success and their ability to compete with other businesses.
The research reveals that there are a number of obstacles to overcome when it comes to the implementation of sustainable supply chains. Significant challenges may be encountered when attempting to manage sustainability across intricate supply chain networks that include a variety of partners and regulatory settings. The gathering of data and maintaining openness may be difficult tasks, which is why effective monitoring and reporting methods are required to guarantee that information on environmental and social behaviors is accurate and dependable. Overcoming a barrier might be necessary for companies, and one of those barriers is getting the alignment and commitment of stakeholders to sustainable practices. In addition, in order for enterprises to maintain their relevance in the ever-changing environment of sustainable supply chain management, they need to adapt to newly emerging trends and advances in technology.
The conversation focuses on developing trends in sustainable supply chains, some of which are highlighted here. The future of sustainable supply chain management is predicted to be shaped by developments in technology such as blockchain, which may increase transparency and traceability; artificial intelligence, which can improve predictive analytics; and the incorporation of sustainability concepts into supply chain operations. The development of legislative frameworks and industry standards will also have an impact on the path that sustainable practices will take in the future. Sodhi and Tang (2016)
In general, both the findings and the conversation highlight how important it is to include methods for social effect and environmental responsibility in supply chain management. The adoption of environmentally responsible business practices in the supply chain enables companies to reduce their impact on the environment, realize cost reductions, improve their brand image, and increase stakeholder engagement. However, there are issues that need to be solved, such as managing complicated networks and maintaining the openness of data. The future of environmentally friendly supply chains will be determined by technological advances and growing sustainability practices. In order to be successful over the long term, businesses will need to adapt to these changes and embrace them.
Figure 2
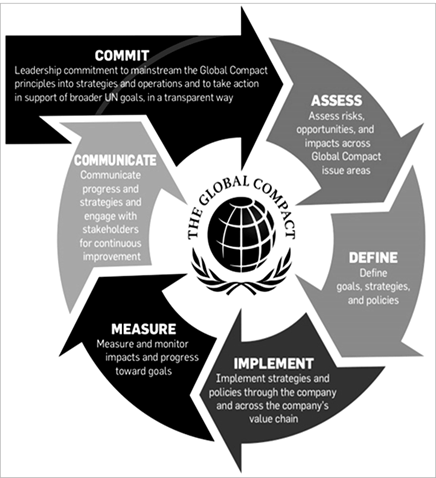
|
Figure 2 Sustainable Supply Chain |
7. CONCLUSION
Crucial issues in today's corporate landscape include the notion of sustainable supply chains and the combination of environmental responsibility and social impact plans. This article has examined the value and relevance of sustainable supply chains, elaborating on the tactics businesses may use to reduce their negative influence on the environment and improve the lives of their communities.
The findings and discussions have highlighted the need of green procurement, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and carbon footprint reduction as environmental responsibility methods for businesses. These methods help businesses lessen their negative effects on the environment, save money, and spread sustainable practices across their supply chains. Organizations may help protect the environment, lessen the likelihood of negative outcomes, and save costs by implementing these measures.
The importance of social impact techniques in environmentally responsible supply chains has also been emphasized. Positive social results can only be achieved via the use of strategies such as enforcing labor standards and human rights, supporting supplier diversity and inclusion, participating in community development efforts, and adopting responsible sourcing. Companies may promote safe and secure workplaces, aid underserved communities, and uphold human rights by implementing these practices across their supply chains.
There are several upsides to using sustainable supply chain methods. Organizations may lessen their vulnerability by fortifying their supply networks against the effects of environmental and societal shocks. Optimizing logistics, cutting down on waste, and making better use of available resources may all lead to significant savings. Long-term financial success and competitiveness may be achieved and brand image can be strengthened when businesses place a premium on sustainability. However, getting to more eco-friendly supply chains isn't a walk in the park. Organizations may have difficulties in, for example, managing complicated supply chain networks, collecting and being transparent with data, aligning with stakeholders, and adjusting to new trends. Commitment, teamwork, and constant progress are essential for overcoming these obstacles. Environmental responsibility and social impact strategies must be included into supply chain management if businesses are to live up to stakeholder expectations and aid in the advancement of sustainable practices. Positive environmental and social consequences, improved brand recognition, and a competitive advantage are all possible when businesses embrace sustainable supply chain methods. Adopting new technologies, adapting to changing regulatory frameworks, and constantly refining sustainability practices are essential for the future of sustainable supply chains. Businesses that make sustainability a top priority now will be better prepared to adapt to the dynamic marketplace of the future.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Aliyu, Y. (2019). Making Corporate Social Responsibility Sustainable in Supply Chains: Cases of Nigerian Pharmaceutical Companies. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Innovative Approaches in Social, Human and Administrative Sciences. SETSCI. https://doi.org/10.36287/setsci.4.8.045
Brandenburg, M., Hahn, G. J., & Rebs, T. (2017). Sustainable Supply Chains: Recent Developments and Future Trends. In Social and Environmental Dimensions of Organizations and Supply Chains (pp. 1–10). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59587-0_1
Gaur, A., & Vazquez-Brust, D. A. (2019). Sustainable Development Goals: Corporate Social Responsibility? A Critical Analysis of Interactions in the Construction Industry Supply Chains Using Externalities Theory. In Greening of Industry Networks Studies (pp. 133–157). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15066-2_8
Liao, C. (2023). An Analysis of Strategies for Adopting Blockchain in Green Supply Chains Under Corporate Social Responsibility. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27050-w
Rodríguez‐González, R. M., Maldonado‐Guzman, G., & Madrid‐Guijarro, A. (2022). The Effect of Green Strategies and Eco‐Innovation on Mexican Automotive Industry Sustainable and Financial Performance: Sustainable Supply Chains as a Mediating Variable. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29(4), 779–794. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2233
Rühmkorf, A. (2015). Consumer Protection Law and Corporate Social Responsibility. In Corporate Social Responsibility, Private Law and Global Supply Chains. Edward Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781783477500.00011
Rühmkorf, A. (2015). Contract Law, Global Supply Chains and Corporate Social Responsibility. In Corporate Social Responsibility, Private Law and Global Supply Chains. Edward Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781783477500.00010
Sodhi, M. S., & Tang, C. S. (2016). Social Responsibility in Supply Chains. In Sustainable Supply Chains (pp. 465–483). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-29791-0_21
Xu, L., Shi, X., Xie, Y., & Tsai, S.-B. (2018). Corporate Social Responsibility-Based Supplier Selection Process in Sustainable Supply Chains. In Advances in Environmental Engineering and Green Technologies (pp. 54–71). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-3537-9.ch003
Xu, L., Shi, X., Xie, Y., & Tsai, S.-B. (2019). Corporate Social Responsibility-Based Supplier Selection Process in Sustainable Supply Chains. In Corporate Social Responsibility (pp. 155–172). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-6192-7.ch009
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2024. All Rights Reserved.