
Exploring the Influence of Digital Marketing on Consumer Behavior and Loyalty
Shams Mukhtar 1![]()
![]() ,
A. Chandra Mohan 2
,
A. Chandra Mohan 2![]() , Dr. Deepti Chandra 3
, Dr. Deepti Chandra 3![]()
1 Ph.D.
Research Scholar, Department of Management, Central University of Tamil Nadu, National
Research Fellow in Institute Public Enterprise (IPE-NRF), India
2 Department
of Management, Central University of Tamil Nadu, Thiruvarur,
610005, India
3 Assistant Professor, Institute of
Public Enterprise, Andhra Pradesh, 500101, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Enterprises have embraced digital marketing as a strategic response to the growing number of consumers on the internet, with the aim of improving their performance. This study aims to deal with the inclinations and reactions of consumers toward a range of digital marketing techniques. The review of existing literature underscores the concept of digital marketing, its capabilities, and the factors influencing consumer conduct, including search engine optimization, intent to purchase, management of customer relationships, buying behavior, satisfaction of customers, and loyalty of customers. Digital marketing encompasses diverse strategies and platforms, such as social media marketing, digital public relations, email marketing, and mobile marketing, which can effectively captivate consumers. The study employs a descriptive research design, obtaining primary data through surveys and in-person interviews. Random sampling is applied, with the participant pool comprising 200 respondents of various ages, genders, educational levels, and occupations. The gathered data is subjected to statistical analysis utilizing techniques like ANOVA and one-sample T-tests. The outcomes show that endorsements from peers and social media platforms significantly impact consumers when making online purchases. Moreover, discounts, rewards, and coupons motivate consumers to review online. Interaction and customization are pivotal drivers for cultivating and sustaining enduring consumer relationships. Marketing professionals should harness digital media and social platforms to facilitate effective communication, augmenting customer satisfaction and loyalty. This inquiry augments comprehension of consumer preferences and reactions to digital marketing tactics. |
|||
|
Received 06 August 2023 Accepted 05 September 2023 Published 30 September 2023 Corresponding Author Shams
Mukhtar, shamsmukhtar@ipeindia.org DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v11.i9.2023.5308 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2023 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Digital Marketing, Consumer Behaviour, Consumer Preferences, Online Shopping, Social Media, Marketing Strategies |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
The quick evolution and progress in information and communication technologies (ICTs) lead to changes in consumers decisions making about buying a product. This encompasses actions such as an information quest, assessing alternatives, and expressing preferences through endorsing desired products and information. consumers are motivated by their own reasons and knowledge. They can search for a company's product or service, chat with others, give ideas, and even get direct replies—all while looking for what they need. Bakhtieva (2017), Noyola-Medina et al. (2018), Teixeira et al. (2018). In this scenario, businesses are encountering a fresh marketing concept that necessitates adapting to unparalleled shifts in the marketing environment. Jackson and Ahuja (2016). The emerging marketing landscape has placed companies in a situation where they need to not only thrive in the traditional competitive sphere but simultaneously establish their presence in the digital-driven marketing realm. Porter (1997) Described as extended rivalry, firm competitiveness entails a heightened level of competition. Consequently, businesses must adapt their strategies to attract new customers, maintain loyalty, and seize opportunities in new markets. In this situation, digital marketing has emerged as a rational solution for companies aiming to enhance their performance by capitalizing on the substantial increase in consumer concentration on the internet, leading to a rise in their interaction with digital media Miklosik et al. (2019).
Online marketing, in its essence, encompasses all marketing techniques executed through electronic devices, which encompasses various online marketing endeavors conducted via the internet. Krishen et al. (2021). According to Scholar et al. (2023), Digital marketing entails utilizing digital channels, such as the internet, mobile devices, display advertisements, and various other digital channels, to advertise and market products or services. Through the incorporation of creative methods that combine technology with conventional marketing techniques, it enables businesses to interact with their customers or clients Wibawa et al. (2021). Digital marketing is a contemporary marketing practise that goes beyond traditional marketing that incorporates digital aspects Mukhtar et al. (2023). Traditional marketing is not meant to be replaced by it; rather, they must coexist with interchangeable roles throughout the consumer experience Kotler et al. (2019). Many institutions, ranging from corporations and healthcare facilities to educational institutions, professional groups, governmental bodies, and non-profit organizations, incorporate digital marketing into their marketing strategies Matosas-López (2021). The primary benefit of embracing digital marketing over traditional marketing lies in its ease of measurement. The extensive data contained within the digital footprint of every internet user can serve as valuable information for competitive analysis.
Embracing online marketing is crucial for companies to enhance their capacity and capabilities amidst intensifying competition characterized by unpredictability. To succeed in this digital era, businesses need to attain digital marketing capabilities through digital transformation. The term "digital marketing capabilities" encompasses the organization's essential assets, including processes, structures, and talents, which enable effective planning and implementation of digital marketing strategies. Chaffey and Smith (2022b). Embarking on a path of transformation, digitalization leverages technology and digital competencies to rethink business models, enhance operational processes, and elevate customer interactions Morakanyane et al. (2020). As digital marketing relies on an information technology infrastructure to store, retrieve, and send data, it is regarded as a part of information technology Stockdale and Standing (2006). The level of adoption of information technology within a firm is influenced by a combination of internal, external, individual, and technological factors. These factors collectively form an adoption ecosystem, which includes elements such as employee attitudes and perceptions, Inner attributes of the company, qualities of the technology itself, industry-specific factors, and broader societal influences. Ezzaouia and Bulchand-Gidumal (2020).
Extensive research has been conducted on various aspects of digital marketing, including the level of adoption, The elements impacting the adoption of digital transformation and capabilities in digital marketing. However, there is still a scarcity of studies that simultaneously explore the interrelationships to establish connections among these concepts and amalgamate them into a unified research mode. Furthermore, past studies in the digital marketing domain have predominantly focused on the customer level, often overlooking the perspective of the firm level Tiago and Veríssimo (2014). The aim of this study is to explore the interconnections among four concepts that have been thoroughly scrutinized by researcher scholars. Additionally, the study's findings are anticipated to make a valuable contribution to the existing knowledge by establishing a model that enhances a firm's digital marketing capabilities through the readiness of its adoption ecosystem and the process of digital transformation.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature review of this study provides an overview of various key concepts related to digital marketing. These concepts include digital marketing itself, digital marketing capabilities, Search Engine Optimization (SEO), purchase intention, customer relationship management, customer buying behavior, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and the factors that contribute to the use of digital marketing. This theoretical framework supports the idea that digital marketing plays a crucial role in capturing consumer attention and creating a competitive advantage for companies.
2.1. DIGITAL MARKETING
According to Piñeiro-Otero and Martínez-Rolán (2016), as also stated by Efficient and effective digital marketing strategies can be executed through the inclusion of a website component and leveraging the internet as a platform for various strategic activities. These activities encompass a range of derivative Examples encompass a wide range, not restricted solely to digital public relations, internet-based advertising, the enhancement of search engine visibility (SEO), Utilizing search engine marketing (SEM) for promotion, leveraging social media as a marketing tool (SMM), and employing email as a marketing channel, electronic newsletters, affiliate marketing, content-driven promotional strategies, and various other approaches Kannan and Li (2017), Rizvanović et al. (2023), (Figure 1)
A website comprises a network of interconnected web pages hosted on a server, serves as a platform for individuals, groups, or organizations to provide information. Typically, websites are hosted on web servers accessible through networks such as the internet or local area networks, identified by Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) Berendt and Spiliopoulou (2000). Companies can create websites as cost-effective marketing tools. The literature emphasizes the importance of incorporating a well-designed website into the marketing activities of an organization, whether related to product or service promotion. Customers tend to favor organizations with well-designes websites Gibson (2018).
Search Data Analysis facilitate tracking activities on a company's website. These analytical tools assist companies in gathering, quantifying, comprehending, assessing, strategizing, documenting, and predicting website performance. Among the web analytics solutions available, Google Analytics stands out as the most significant Bala and Verma (2018). Advertisers should utilize digital analytics to comprehensively understand their business, improve return on investment (ROI), and enhance conversions.
Figure 1
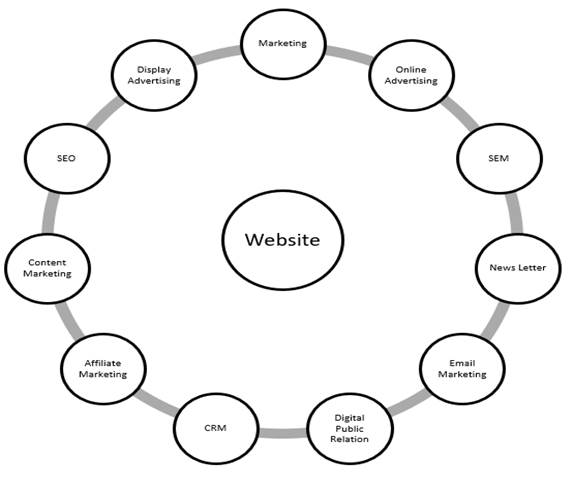
|
Figure 1 Approach for Effective Digital Marketing Strategy Gibson (2018) |
Effective utilization of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a pivotal role in generating traffic for websites. It encompasses enhancing a website or webpage's prominence in the search outcomes of unpaid and natural search engines. Achieving a superior position in these search results in greater traffic coming from individuals who use search engines. Search engine optimization (SEO) techniques cover a variety of search kinds, including picture, local, video, academic, and news searches. Yasmin et al. (2015). Key SEO tactics, as mentioned Giomelakis and Veglis (2016), include proper website indexing, incorporating relevant keywords, customizing website content, and ensuring the uniqueness of site content. To increase consumer participation in their digital marketing activities, In addition, companies employ strategies such as social media promotion, email-based campaigns, digital public relations, and mobile marketing Viglia (2014). Utilizing social media involves harnessing the power of Instagram, Facebook, Google, LinkedIn, and Twitter to enhance brand visibility and expand the reach to consumers. Email marketing facilitates businesses in connecting with a wider range of consumers by disseminating information and messages via email Makrides et al. (2020). Publishing PR content in online directories, distributing press releases online, delivering marketing communication through films or music, and participating in diverse discussion platforms are all steps in establishing an online public relations presence Bala and Verma (2018). Additionally, cellular/mobile marketing has developed into a ground-breaking discipline in market that makes it possible for companies and customers to communicate with each other through mobile devices. This comprises websites, applications, and content optimized for mobile devices. Through mobile advertising, businesses can establish connections with customers using mobile devices, delivering relevant messages at the right time and location Azimi (2021).
2.2. PURCHASE INTENTION
The advancement of digital marketing and the growth of online sales have influenced purchase intentions a crucial factor. Purchase intention is a complex process influenced by consumer behavior, perception, and attitude Kim and Lennon (2008). Factors such as price comparison, perceived value, and quality directly impact purchase intention Peng et al. (2019). Customers frequently perceive inexpensive goods with poor packaging and unknown brand as less trustworthy and risky Mirabi et al. (2015). External factors, such as website information, and internal factors, such as the shopping experience, also shape purchase intention Shang et al. (2005). A visually appealing website with user-friendly online services and layout can enhance customer motivation and objective to visit the website for searching and buying products. Multiple stages of purchase intention, influenced by elements such as expertise, existing knowledge, personal interests, inclinations, persuasiveness, and the ability to influence purchasing decisions, are observed before the final purchase assessment Hsu et al. (2013). Online information searching makes buying goods and services more satisfying and enjoyable. It encourages repeat purchases, visits to the online platform, as well as favourable referrals and product reviews for the promoted goods Sohn and Kim (2020). Research conducted by Dehghani and Tumer (2015) demonstrated that branding significantly impacts purchase intention in the digital marketing context. As consumer trends evolve, online product reviews have become an essential reference point for making informed purchase decisions.
2.3. BUYING BEHAVIOUR OF CUSTOMERS
The buying behavior of individuals plays a significant role in consumer behavior, both in general and among specific customer segments Bian and Moutinho (2011). Marketing strategies targeting buying behavior aim to establish connections between products in the market and specific consumer groups Vinson et al. (1977). This involves segmenting the market based on dimensions of buying behavior, strategically positioning products to resonate with the behaviors, hobbies, viewpoints of the intended audience and implementing tailored promotional campaigns that leverage buying behavior appeals to enhance the market value of the product. In India, the Internet has existed for approximately 20 years, and It ranks within the top three nations globally in the number of internet users, boasting 145 million consumers Anand et al. (2018). However, digital marketing only represents a small percentage (3-4%) of organized retailing in the country Kumar and Dange (2014). This indicates that certain factors hinder the growth of online marketing in India, one of which is the perceived risk among the youth. Despite the potential of online shopping in India, driven by its large youth population, organized retailing faces challenges in reaching rural areas. In contrast, online retailers are finding buyers in urban and rural regions nationwide. Consumer purchase decisions are often influenced by emotional attachment to brands Niazi et al. (2012). The government is making substantial investments in internet infrastructure, further facilitating the growth of online commerce.
2.4. CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
Customer satisfaction is crucial for companies seeking lasting consumer relationships. It's gauged by assessing consumer expectations against actual performance and service quality Caruana (2002). The Expectancy Disconfirmation Model defines satisfaction as comparing expectations with performance Van-Ryzin (2013). When performance meets or exceeds expectations, customer satisfaction arises, bolstering business success, profitability, repeat patronage, and brand loyalty Diez-Martin et al. (2019). Satisfaction influences favorable intentions and attitudes, reflecting positive buying experiences derived from comparing expectations to actual offerings. Positive confirmation happens when perceived performance exceeds expectations, resulting in satisfaction Royle and Laing (2014). Conversely, negative confirmation occurs when perceived performance falls short, leading to dissatisfaction. Researchers define customer satisfaction as gauging consumer reactions to a product and emotions stemming from expectation-based performance Tiago and Veríssimo (2014). Another definition emphasizes fair treatment's role, where satisfaction springs from perceived fairness and drives repurchasing and reuse Román (2003). Satisfied customers exhibit loyalty, driving profitability through repeat purchases, positive word-of-mouth, and focus on the company.
2.5. CUSTOMER LOYALTY
Customer loyalty, a valuable intangible asset impacting company profitability, has garnered attention from scholars and marketing experts. Definitions vary, with some viewing it as an emotional connection beyond transactions Uncles et al. (2003). This loyalty drives growth, irrespective of situations, bolstering the company's prospects. Oliver's model is widely used Evanschitzky et al. (2012), recognizing active and passive loyalty. In today's digital age, active loyalty, especially pertinent due to online platforms, holds greater importance. Scholars remain captivated by loyalty's implications, aiming to unravel antecedents and intricate relationships Ilyas et al. (2021). Researchers stress understanding customer needs, influencing factors, attitudes, and purchasing behaviors. Highlighted by Bowen and Chen (2001) customer loyalty confers competitive advantage and business success, urging practitioners to devise intelligent strategies for fostering and retaining loyalty.
2.6. DIGITAL MARKETING CAPABILITIES
Digital marketing capabilities encompass an organization’s capacity to utilize online and digital technologies to foster meaningful engagements with consumers, as defined by Trainor et al. (2011). Through these interactions, customers can access company resources and information, while firms gain valuable insights into their customer base, as highlighted by Herhausen et al. (2020). Chaffey and Smith (2022b) further describe digital marketing capabilities as the company's capacity of the company to strategically devise and carry out digital marketing initiatives. These abilities cover the core procedures, frameworks, and competencies that act as vital resources for businesses to excel in the digital world (Figure 2).
Figure 2
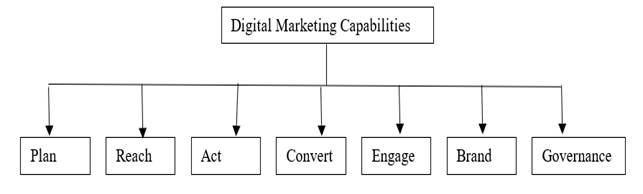
|
Figure 2 Digital Marketing Capabilities Framework Apasrawirote et al. (2022) |
There are seven criteria used to evaluate a digital marketing capacity, which are listed below:
1) Planning: Developing a comprehensive plan to incorporate digital marketing across all organizational strategies.
2) Reach: Enhancing awareness and attracting Increasing the number of website visitors through successful marketing communication
3) Action: Engaging with customers on internet to generate leads and foster meaningful interactions.
4) Conversion: Enhancing the effectiveness of sales channels such as email, website, and targeting to successfully convert leads into purchases.
5) Engage: Enhancing customer retention and encouraging repeat purchases by putting in place methods and procedures that foster consumer loyalty and support.
6) Brand: Forming an emotional bond with clients by utilizing more frequent interaction and communication through internet channels that emphasize the company's distinctive value offer.
7) Governance: Executing digital transformation strategies that smoothly incorporate digital media, technology, and data into the company. This requires the strategic alignment of appropriate staff, procedures, marketing tools, and data to efficiently conduct digital marketing initiatives.
3. RESEARCH METHOD
The study employed a Descriptive Design methodology, gathering information from both Primary and Secondary sources. Primary Data was gathered through surveys and face-to-face interviews using a structured questionnaire for Providing predefined options for participants to select from. We gathered secondary information from various sources such as books, the internet, digital platforms, and social media websites. Random sampling was employed, with a sample size of 200 respondents. Out of these, 160 respondents completed the questionnaire, 40 people submitted their comments via Google Docs. The sample had 108 females and 92 males with ages ranging from 16 to 55. The education level of the respondents varied, including high school, intermediate, graduate, and post-graduate. The study included respondents from different parts of Tamil Nadu, specifically Thiruvarur District, Central University of Tamil Nadu, Mayiladutrai, and Trichy. Survey responses form the basis for gathering primary data, which is subsequently processed through software tools like SPSS and Microsoft Excel for analysis. The study also examined website features that attract the attention of digital media users towards digital marketing. Using a Likert scale, respondents gave average comments on various website aspects, where a rating of 1 indicated a strong disagreement of opinion, while a rating of 5 signified a strong agreement of opinion. Through ANOVA analysis, it was determined that there is a significant difference in consumer responses to website features that grab their attention. Incorporating the term 'complimentary or free' into website content and ensuring a sleek and minimalist website design were proven to be ineffective in attracting users. Interactive websites and personalization, on the other hand, were shown to be effective.
4. RESULTS AND FINDINGS
Based on age-related statistics of Internet users in Tamil Nadu, the questionnaire was distributed to different age groups. The plurality of respondents (44.6%) had a bachelor's degree, followed by those with a diploma (37.1%), a master's degree (17.3%), and a PhD (1%). According to occupation, the student’s category donated the most (38%), then businesses (18.5%), government employees (12.5%), doctors (6%), others (12%), and businesses. Selection of respondents was based on the randomness and exploratory study of literatures, which is accurate with this research in Tamil Nadu context. Apart from this Major e-commerce consumers were well versed in understanding and responding about the concept of this study. According to respondents' marital status, married respondents made up the majority (56.7%), followed by single respondents.
In this research, an examination of consumer demographics is conducted, encompassing factors such as age, gender, educational background, income, occupation and consumers knowledge about the digital knowledge completed so far. Most of the Consumers for this study are between aged 16-25 account for 37.5% of the group, with 26-35-year-olds comprising 26.5%, while those in the 46-55 age bracket make up only 15%. Females are 54% whereas males are 46%. Different hypothesis provides following results.
|
Table 1 Information on the Respondent’s Profile |
|||
|
Variables |
Measuring Group |
Frequency |
Percentage % |
|
Age Group |
16 to 25 |
75 |
37.50% |
|
26 to 35 |
53 |
26.50% |
|
|
36 to 45 |
42 |
21% |
|
|
46 to 55 |
30 |
15% |
|
|
Total |
200 |
100% |
|
|
Gender |
Male |
92 |
46% |
|
Female |
108 |
54% |
|
|
Total |
200 |
100% |
|
|
Income Level |
Below 1,00,000 |
13 |
11% |
|
1,00,001 to
3,00,000 |
34 |
28% |
|
|
3,00,001 Above |
73 |
61% |
|
|
Total |
200 |
100% |
|
|
Aware about Digital
Marketing Platforms |
YES |
200 |
100% |
|
NO |
0 |
0% |
|
|
TOTAL |
120 |
100% |
|
|
Social Media User |
YES |
200 |
100% |
|
NO |
0 |
0% |
|
|
TOTAL |
120 |
100% |
|
|
Occupation |
Private Sector
Service |
37 |
18.50% |
|
Government Employee |
25 |
12.50% |
|
|
Business |
26 |
13% |
|
|
Students |
76 |
38% |
|
|
Doctor |
12 |
6% |
|
|
Other |
24 |
12% |
|
|
TOTAL |
200 |
100% |
|
The data provides
information about the frequencies and percentages of different variables within
a group, including age groups, gender, income levels, awareness about digital
marketing platforms, social media usage, and occupations.
H1: Factor
affecting online frequency shopping
The impact of gender on online shopping frequency was examined, and the analysis unveiled no noteworthy correlation with statistical significance. This implies that there is no noticeable distinction between males and females in terms of how often they visit online shopping websites. Both genders engage in online shopping with similar levels of frequency.
Table 2
|
Table 2 |
|
|
Marketing methods |
Mean |
|
Blogs |
3.75 |
|
Magazine and newspaper ads |
5.38 |
|
emails from businesses |
5.45 |
|
TV ads |
4.82 |
|
ads on external websites |
4.60 |
|
Friends' recommendations |
1.93 |
|
social media platforms |
2.09 |
H2: Marketing channels that influence Consumers when buying online
Respondents rated various marketing methods, revealing distinct preferences. Magazine and newspaper ads (5.38) and emails from businesses (5.45) received high ratings, signifying their effectiveness. TV ads (4.82) and ads on external websites (4.60) were deemed moderately effective. In contrast, friends' recommendations (1.93) and social media platforms (2.09) scored lower, suggesting they are less valued by respondents. Blogs (3.75) fell in the middle, indicating moderate effectiveness. This data illustrates the varying perceived values of these marketing approaches, with magazine ads and business emails standing out as particularly effective, while friends' recommendations and social media lag behind in respondents' eyes.
When it comes to buying online, marketers utilize various marketing channels to reach customers and promote their products. Table 2 provides insights into the influence of different channels on consumers. The second most influential channel is social networking platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, as these platforms attract a highly engaged audience. On the other hand, Retailer emails have the least impact on consumers. Additionally, magazine and newspaper advertisements have no impact on online shopping.
Table 3
|
Table 3 |
|
|
Strategies for advertisement |
Mean |
|
Obtaining Coupons |
4.13 |
|
Ads on side panel |
3.54 |
|
YouTube ads |
3.44 |
|
Updates on Receiving Email |
2.57 |
|
Games forms ads |
2.63 |
|
Pop-up Ads |
2.06 |
|
TOTAL |
3.06 |
H3: Different Online Advertising Strategy Preferred by Consumers
In assessing advertising strategies, obtaining coupons emerged as the frontrunner with a solid rating of 4.13, indicating moderate effectiveness and favorability among respondents. Conversely, ads on side panels earned a rating of 3.54, implying slightly lower effectiveness when compared to coupons. YouTube ads followed closely at 3.44, signifying a moderate level of effectiveness. Updates received via email marketing garnered a lower score of 2.57, portraying a lesser degree of effectiveness. Advertising through games or in-game forms secured a rating of 2.63, suggesting it was less effective in the respondents' eyes. Pop-up ads, with the lowest rating of 2.06, were perceived as the least effective among the strategies. The overall average rating for all strategies, standing at 3.06, serves as a comprehensive measure of the perceived effectiveness and favorability of these advertising strategies in the study.
Various online advertising strategies were examined to determine consumer preferences. Table 3 illustrates the results, indicating that the most preferred online strategy, as confirmed by the test, is obtaining online coupons. This is succeeded by advertisements in side panels and on YouTube. Conversely, pop-ups were found to be the least significant strategy among consumers.
Table 4
|
Table 4 |
||
|
Strategies |
Mean |
Sig.(2-tailed) |
|
Avoid pop-ups on website |
4.36 |
.000 |
|
Avoid non-closable browser |
4.25 |
.000 |
|
Avoid obligatory software downloads |
4.14 |
.000 |
|
Avoid blinking elements |
3.88 |
.000 |
|
Avoid sponsored link |
3.61 |
.000 |
H4: Strategies in digital marketing that marketers should avoid
In assessing website strategies, it's clear that avoiding pop-ups (mean rating: 4.36) and non-closable browsers (mean rating: 4.25) is paramount, with respondents finding these highly effective and statistically significant (p < 0.001). Similarly, steering clear of obligatory software downloads (mean rating: 4.14) and blinking elements (mean rating: 3.88) garners strong favor, marked by their high effectiveness and statistical significance. In contrast, while avoiding sponsored links (mean rating: 3.61) received a lower rating, it remains statistically significant. These findings emphasize the crucial role of user-friendly website design in enhancing user experience and satisfaction, as reflected by both mean ratings and rigorous statistical analysis.
Based on the findings of a one-sample T-test, Table 4 highlights various digital marketing strategies that marketers should steer clear of. The results indicate that all the strategies are statistically significant. It can be deduced that consumers are in agreement that Marketers must avoid employing not just pop-ups on websites, but also inescapable windows and obligatory software downloads. Pop-ups are considered intrusive and lead to annoyance, similar to the un-closable windows and mandatory software downloads. On the other hand, flashing items and links to sponsors are still tolerable to some extent.
Table 5
|
Table 5 |
|||
|
Which incentives are important to
repeatedly visit a website? |
Mean |
t |
Sig. (2 tailed) |
|
Competitive pricing |
4.48 |
38.796 |
.000 |
|
Efficient shipping price |
3.77 |
14.176 |
.000 |
|
Coupon Voucher |
4.16 |
23.273 |
.000 |
|
Incentives for repeat customers |
3.60 |
12.760 |
.000 |
|
Complimentary items |
4.19 |
21.935 |
.000 |
|
Personalization |
4.00 |
16.511 |
.000 |
|
Revised product details |
3.56 |
11.824 |
.000 |
|
Favorable refund policy |
3.72 |
14.200 |
.000 |
|
Website is Interactive |
3.49 |
10.560 |
.000 |
H6: Incentives
Important for Consumers That Prompt Repeat Visits to Website
Customers highly prioritize competitive pricing (mean rating: 4.48), revealing its paramount importance for website revisit motivation. This preference is emphatically backed by a substantial t-value of 38.796 and an exceptionally low p-value of .000, signifying its statistical significance. Efficient shipping pricing follows closely (mean: 3.77), remaining above average and statistically significant with a t-value of 14.176 and a p-value of .000. Coupon vouchers also wield substantial influence (mean: 4.16) as indicated by a high mean rating and corroborated by a noteworthy t-value of 23.273 and a p-value of .000. While slightly less crucial, incentives for repeat customers (mean: 3.60) are still considered important, with a significant t-value of 12.760 and a p-value of .000. Complimentary items (mean: 4.19) hold considerable weight, backed by a robust t-value of 21.935 and a p-value of .000. Personalization (mean: 4.00) is similarly pivotal, supported by a t-value of 16.511 and a p-value of .000. Revised product details (mean: 3.56) maintain importance, substantiated by a t-value of 11.824 and a p-value of .000. Favorable refund policies (mean: 3.72) are significant with a t-value of 14.200 and a p-value of .000. Lastly, an interactive website (mean: 3.49) remains a pertinent factor, supported by a t-value of 10.560 and a p-value of .000.
Based on the results of a one-sample T-test, it is evident from Table 5 that different incentives that encourage consumers to visit a website repeatedly are statistically significant. Values of mean suggest that personalization, competitive pricing, and Complimentary items, coupons are the most impactful incentives for encouraging repeat visits to a website. Additionally, consumers consider favorable refund policies, rewards for repeat customers, and Efficient shipping price to be somewhat important factors that contribute to their repeated visits to a website.
Table 6
|
Table 6 |
||
|
Motivating Factors |
Mean |
Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
I get discount in exchange for writing
review |
4.20 |
.000 |
|
I get reward or reward points for
giving a review |
4.00 |
.000 |
|
I found coupon in exchange for writing
a review |
3.84 |
.000 |
H7: Factors That Motivates
Consumers to Write Reviews
The analysis conducted using a one-sample T test revealed that certain factors that motivate consumers to write reviews, including receiving discounts, reward points, and coupons, were found to be statistically significant based on the data presented in Table 6.
Customers highly value incentives for writing reviews, with getting a discount (mean rating 4.20) emerging as the most influential factor. This is underscored by the remarkably low p-value of .000, affirming the strong preference for discounts in exchange for reviews. Rewards or reward points (mean rating 4.00) also hold significant sway, as evidenced by the small p-value of .000, reinforcing their importance. While slightly lower, finding a coupon (mean rating 3.84) remains a potent motivator for customers, with a statistically significant preference indicated by the p-value of .000. In summary, these incentives are vital drivers of customer reviews, with discounts leading the way, followed closely by rewards and coupons.
5. FINDINGS
Based on a comprehensive analysis of demographic data and consumer preferences, several key findings have emerged. The study surveyed respondents across different age groups, educational backgrounds, and occupations in Tamil Nadu. Notably, the majority of respondents held bachelor's degrees, and a significant portion were students. When considering age, the study found that a considerable number of consumers fell into the 16-25 age group, with a fairly even gender distribution.
In terms of online shopping behavior, the study revealed that gender did not significantly impact the frequency of online shopping, indicating that both males and females engage in online shopping with similar frequencies.
This study examines the preferences and responses of consumers towards digital marketing strategies. The study found that when making online purchases, consumers are primarily swayed by suggestions from friends, peers, and social media platforms. They exhibit a preference for side-panel ads and online coupons, yet they express annoyance with pop-up ads, un-closable windows, and email updates. Customers are drawn in by incentives like complimentary giveaways, loyalty rewards, and competitive pricing, which serve as motivation for them to share online reviews, particularly when they are presented with discounts or coupons. Maintaining long-term customer relationships requires companies to enable effective communication with customers using digital media and social platforms. The findings of this study have important implications for marketers who are looking to reach and engage consumers in the digital age. By understanding the preferences and responses of consumers, marketers can develop more effective digital marketing approaches aimed at attaining their corporate objectives.
Regarding marketing channels influencing consumers when buying online, magazine and newspaper ads, as well as emails from businesses, were rated highly effective, while friends' recommendations and social media platforms received lower ratings. Different online advertising strategies were also explored, with obtaining coupons emerging as the most preferred strategy among consumers. On the flip side, pop-up ads were deemed the least effective. Additionally, the study identified critical website strategies to avoid, emphasizing the importance of user-friendly design. Finally, incentives that encourage repeat visits to websites were examined, with competitive pricing and coupon vouchers standing out as highly impactful motivators.
The study has several limitations worth noting. First, the study's reliance on a specific demographic of Internet users in Tamil Nadu may limit the generalizability of its findings to a broader population. The sample may not represent the diverse range of Internet users in other regions or countries. Second, the study's questionnaire-based approach may introduce response bias, as respondents may provide socially desirable answers, or their perceptions may not accurately reflect their actual behavior. Additionally, the study does not delve into the reasons behind certain preferences, leaving a gap in understanding the underlying motivations. Furthermore, while the statistical analysis provides valuable insights, it does not account for potential confounding variables that could influence the observed relationships. Finally, the study primarily focuses on consumer perceptions and preferences, which may not always align with actual behavior. Despite these limitations, the study offers valuable insights into the preferences and perceptions of the surveyed population regarding various marketing strategies, digital incentives, and online shopping factors.
7. CONCLUSION
This study underscores the pivotal role of digital marketing in today's business landscape, emphasizing the need for seamless integration and a deep understanding of consumer behavior. By exploring the dynamics between digital marketing strategies, consumer preferences, and capabilities, this research highlights the path to successful digital endeavors. In a world shaped by rapid technological advancements, embracing the digital realm has become imperative for businesses. Digital marketing encompasses a wide array of strategies, from social media promotions to SEO and email campaigns, all underpinned by valuable user data. This adaptability empowers companies to thrive amidst fierce competition. Critical to this journey is digital transformation, harnessing technology to enhance business models, processes, and customer experiences. The study reveals the significant influence of peer recommendations and social media on online shopping decisions, along with the appeal of interactive and personalized websites. Competitive pricing, coupons, and freebies drive repeat visits, while discounts and rewards motivate online reviews. These insights offer a roadmap for effective digital strategies, emphasizing the importance of tailoring approaches to consumer preferences.
In this dynamic digital landscape, understanding the diverse facets of consumer behavior and preferences is paramount. Tailored marketing strategies, user-friendly website design, and incentives for engagement hold the keys to lasting success. By aligning with these findings, businesses and marketers can effectively connect with their target audience and cultivate enduring customer relationships. Ultimately, this study provides invaluable guidance for navigating the digital landscape and meeting the evolving needs of consumers in Tamil Nadu.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Amofah, P., & Ijaz, A. (2005). Objectives, Strategies and Expected Benefits of Customer Relationship Management.
Anand, N., Thomas, C., Jain, P. A., Bhat, A., Thomas, C., Prathyusha, P. V., Aiyappa, S., Bhat, S., Young, K., & Cherian, A. V. (2018). Internet Use Behaviors, Internet Addiction and Psychological Distress Among Medical College Students: A Multi Centre Study from South India. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 37, 71-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2018.07.020
Apasrawirote, D., Yawised, K., & Muneesawang, P. (2022). Digital Marketing Capability : The Mystery of Business Capabilities. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 40(4), 477-496. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-11-2021-0399
Azimi, M. K. (2021). Factors Affecting Intentions and Attitudes of Afghan and Turkish Consumers Towards Mobile Marketing Applications.
Bakhtieva, E. (2017). B2B Digital Marketing Strategy: A Framework for Assessing Digital Touch Points and Increasing Customer Loyalty Based on Austrian Companies from Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Industry. Oeconomia Copernicana, 8(3), 463-478. https://doi.org/10.24136/oc.v8i3.29
Bala, M., & Verma, D. (2018). A Critical Review of Digital Marketing. (SSRN Scholarly Paper No. 3545505), 8(10), 321-339.
Berendt, B., & Spiliopoulou, M. (2000). Analysis of Navigation Behaviour in Web Sites Integrating Multiple Information Systems. The VLDB Journal, 9(1), 56-75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007780050083
Bian, X., & Moutinho, L. (2011, February 15). The Role of Brand Image, Product Involvement, and Knowledge in Explaining Consumer Purchase Behaviour of Counterfeits : Direct and Indirect Effects. European Journal of Marketing, 45(1/2), 191-216. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090561111095658
Bowen, J. T., & Chen, S. (2001,September 1). The Relationship Between Customer Loyalty and Customer Satisfaction. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 13(5), 213-217. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596110110395893
Caruana, A. (2002, August 1). Service Loyalty : The Effects of Service Quality and the Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction. European Journal of Marketing, 36(7/8), 811-828. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090560210430818
Chaffey, D., & Smith, P. R. (2022b, July 22). Digital Marketing Excellence: Planning, Optimizing and Integrating Online Marketing. Taylor & Francis, 676. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003009498
Diez-Martin, F., Blanco-Gonzalez, A., & Prado-Roman, C. (2019). Research Challenges in Digital Marketing. Sustainability, 11(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102839
Dehghani, M., & Tumer, M. (2015, August). A Research on Effectiveness of Facebook Advertising on Enhancing Purchase Intention of Consumers. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 597-600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.03.051
Dastane, D. O. (2020, September 16). Impact of Digital Marketing on Online Purchase Intention : Mediation Effect of Customer Relationship Management, 10(1), 142-158.
Evanschitzky, H., Ramaseshan, B., Woisetschläger, D. M., Richelsen, V., Blut, M., & Backhaus, C. (2012). Consequences of Customer Loyalty to the Loyalty Program and to the Company. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(5), 625-638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-011-0272-3
Ezzaouia, I., & Bulchand-Gidumal, J. (2020, April). Factors Influencing the Adoption of Information Technology in the Hotel Industry. An Analysis in a Developing Country. Tourism Management Perspectives, 34, 100675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2020.100675
Gibson, C. (2018). The Most Effective Digital Marketing Strategies & Approaches : A Review of Literature, 8(2), 12-574.
Giomelakis, D., & Veglis, A. (2016). Investigating Search Engine Optimization Factors in Media Websites. Digital Journalism, 4(3), 379-400. https://doi.org/10.1080/21670811.2015.1046992
Herhausen, D., Miočević, D., Morgan, R. E., & Kleijnen, M. H. P. (2020 October). The Digital Marketing Capabilities Gap. Industrial Marketing Management, 90, 276-290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.07.022
Hsu, C., Chuan-Chuan Lin, J., & Chiang, H. (2013, January 25). The Effects of Blogger Recommendations on Customers' Online Shopping Intentions. Internet Research, 23(1), 69-88. https://doi.org/10.1108/10662241311295782
Ilyas, G. B., Munir, A. R., Tamsah, H., Mustafa, H., & Yusriadi, Y. (2021). The Influence of Digital Marketing and Customer Perceived Value Through Customer Satisfaction on Customer Loyalty. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24 Pt. 2, 1.
Jackson, G., & Ahuja, V. (2016). Dawn Of The Digital Age and the Evolution of the Marketing Mix. Journal of Direct, Data and Digital Marketing Practice, 17(3), 170-186. https://doi.org/10.1057/dddmp.2016.3
Kannan, P. K., & Li, H. A. (2017, March). Digital Marketing: A Framework, Review and Research Agenda. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 34(1), 22-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2016.11.006
Kim, M., & Lennon, S. (2008, January 11). The Effects of Visual and Verbal Information on Attitudes and Purchase Intentions in Internet Shopping. Psychology & Marketing, 25(2), 146-178. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.20204
Krishen, A. S., Dwivedi, Y. K., Bindu, N., & Kumar, K. S. (2021, July). A Broad Overview of Interactive Digital Marketing: A Bibliometric Network Analysis. Journal of Business Research, 131, 183-195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.03.061
Kumar, D. V., & Dange, U. (2014, November 3). E-Retailing in India-A Study of Consumers' Internet Usage Pattern, their Profile and their Shopping Pattern. (SSRN Scholarly Paper No. 2518295). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2518295
Hsi-Peng L., & Yu-Jen, P. S. (2009, August 14). Factors Affecting Purchase Intention on Mobile Shopping Web Sites. Internet Research, 19(4), 442-458. https://doi.org/10.1108/10662240910981399
Makrides, A., Vrontis, D., & Christofi, M. (2020). The Gold Rush of Digital Marketing : Assessing Prospects of Building Brand Awareness Overseas. Business Perspectives & Research, 8(1), 4-20. https://doi.org/10.1177/2278533719860016
Matosas-López, L. (2021, March). The Management of Digital Marketing Strategies in Social Network Services : A Comparison Between American and European Organizations. Journal of Open Innovation : Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010065
Miklosik, A., Kuchta, M., Evans, N., & Zak, S. (2019, June 26). Towards the Adoption of Machine Learning-Based Analytical Tools in Digital Marketing. IEEE Access, 7, 85705-85718. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924425
Mirabi, V., Akbariyeh, H., & Tahmasebifard, H. (2015 January). A Study of Factors Affecting on Customers Purchase Intention. 2(1).
Morakanyane, R., O'Reilly, P., Mcavoy, J., & Grace, A. (2020). Determining Digital Transformation Success Factors. https://doi.org/10.24251/HICSS.2020.532
Mukhtar, S., Vigneshwari, K., & Mohan, A. C. (2023). Social Media Relevance for Business, Marketing and Preferences for Customers. 58(157).
Niazi, G. S. K., Siddiqui, J., Alishah, B., & Hunjra, A. I. (2012, August 16). Effective Advertising and its Influence on Consumer Buying Behavior (SSRN Scholarly Paper No. 2130358), 4(3), 114-119.
Noyola-Medina, A., Pinzon-Castro, S., & Maldonado-Guzman, G. (2018). Innovation and Digital Marketing Adoption in Mexican Small Business. Journal of Management and Sustainability, 8(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.5539/jms.v8n2p18
Nuseir, M., & Refae, G. E. (2022). The Effect of Digital Marketing Capabilities on Business Performance Enhancement : Mediating the Role of Customer Relationship Management (CRM). International Journal of Data and Network Science, 6(2), 295-304. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2022.1.008
Nylén, D., & Holmström, J. (2015, January-February). Digital Innovation Strategy: A Framework for Diagnosing and Improving Digital Product and Service Innovation. Business Horizons, 58(1), 57-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.09.001
Peng, L., Zhang, W., Wang, X., & Liang, S. (2019, March). Moderating Effects of Time Pressure on the Relationship Between Perceived Value and Purchase Intention in Social E-Commerce Sales Promotion : Considering the Impact of Product Involvement. Information & Management, 56(2), 317-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2018.11.007
Piñeiro-Otero, T., & Martínez-Rolán, X. (2016, February 3). Understanding Digital Marketing-Basics and Actions. In C. Machado & J. P. Davim (Eds.), Mba: Theory and Application of Business and Management Principles. Springer International Publishing, 37-74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28281-7_2
Porter, M. E. (1997). Competitive Strategy. Measuring Business Excellence, 1(2), 12-17. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb025476
Richards, K. A., & Jones, E. (2008 April). Customer Relationship Management : Finding Value Drivers. Industrial Marketing Management, 37(2), 120-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2006.08.005
Rizvanović, B., Zutshi, A., Grilo, A., & Nodehi, T. (2023, Janauary). Linking the Potentials of Extended Digital Marketing Impact and Start-Up Growth: Developing a Macro-Dynamic Framework of Start-Up Growth Drivers Supported by Digital Marketing. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 186, 122128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122128
Román, S. (2003). The Impact of Ethical Sales Behaviour on Customer Satisfaction, Trust and Loyalty to the Company : An Empirical Study in the Financial Services Industry. Journal of Marketing Management, 19(9-10), 915-939. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257X.2003.9728245
Royle, J., & Laing, A. (2014, April). The Digital Marketing Skills Gap : Developing a Digital Marketer Model for the Communication Industries. International Journal of Information Management, 34(2), 65-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2013.11.008
Ryals, L., & Payne, A. (2001). Customer Relationship Management in Financial Services : Towards Information-Enabled Relationship Marketing. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 9(1), 3-27. https://doi.org/10.1080/713775725
Scholar, Krishnamurthy, V., Mohan, A. C., & Mukhtar, M. S. (2023). Social Media Relevance for Business, Marketing and Preferences for Customers. Manager- The British Journal of Administrative Management, 58(157), 39-52.
Kotler, P. Setiawan, Kartajaya, H. & Setiawan, I. (2019). Marketing 4.0: Bergerak Dari Tradisional ke Digital. Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Rong-An, S., Yu-Chen, C., & Shen, L. (2005, March). Extrinsic Versus Intrinsic Motivations for Consumers to Shop On-Line. Information & Management, 42(3), 401-413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2004.01.009
Sohn, J. W., & Kim, J. K. (2020, November). Factors that Influence Purchase Intentions in Social Commerce. Technology in Society, 63, 101365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101365
Stockdale, R., & Standing, C. (2006, September 16). An Interpretive Approach to Evaluating Information Systems : A Content, Context, Process Framework. European Journal of Operational Research, 173(3), 1090-1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2005.07.006
Teixeira, S., Branco, F., Martins, J., Au-Yong-Oliveira, M., Moreira, F., Goncalves, R., Perez-Cota, M., & Jorge, F. (2018, June 28). Main Factors in the Adoption of Digital Marketing in Startups an Online Focus Group Analysis. 2018 13th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.23919/CISTI.2018.8399435
Tiago, M. T. P. M. B., & Veríssimo, J. M. C. (2014, November-December). Digital Marketing and Social Media : Why Bother ? Business Horizons, 57(6), 703-708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.07.002
Trainor, K. J., Rapp, A., Beitelspacher, L. S., & Schillewaert, N. (2011, January). Integrating Information Technology And Marketing : An Examination of the Drivers and Outcomes of E-Marketing Capability. Industrial Marketing Management, 40(1), 162-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2010.05.001
Uncles, M. D., Dowling, G. R., & Hammond, K. (2003). Customer Loyalty and Customer Loyalty Programs. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 20(4), 294-316. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363760310483676
Van-Ryzin, G. G. (2013, April 30). An Experimental Test of the Expectancy-Disconfirmation Theory of Citizen Satisfaction. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, 32(3), 597-614. https://doi.org/10.1002/pam.21702
Viglia, G. (2014). Online Marketing Communication Channels. In G. Viglia (Ed.), Pricing, Online Marketing Behavior, and Analytics. Palgrave Macmillan US. 23-38. https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137413260_3
Vinson, D. E., Scott, J. E., & Lamont, L. M. (1977, April). The Role of Personal Values in Marketing and Consumer Behavior. Journal of Marketing, 41(2), 44-50. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224297704100215
Wibawa, R. C., Pratiwi, C. P., & Larasati, H. (2021). The Role of Nano Influencers Through Instagram as an Effective Digital Marketing Strategy. 233-238. https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.211207.036
Yasmin, A., Tasneem, S., & Fatema, K. (2015, April). Effectiveness of Digital Marketing in the Challenging Age: An Empirical Study. The International Journal of Management Science and Business Administration, 1(5), 69-80. https://doi.org/10.18775/ijmsba.1849-5664-5419.2014.15.1006
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2023. All Rights Reserved.