
EVALUATION OF INTEGRATED APPROACH OF PSYCHO AND YOGA THERAPY IN MANAGEMENT OF ANXIETY NEUROSIS: A CASE STUDY
1 Assistant
Professor, Department of Psychology Dev Sanskriti Vishwavidyalaya, Haridwar,
Uttarakhand, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Case study of
a 45-year-old male patient with sedentary lifestyle, diagnosed with anxiety
disorder (Neurosis) and other anxiety related problems since 2004. He
undergone with integrated approach of psycho & yoga therapy (IAPYT) for
15 days at Psycho Clinic, Dev Sanskriti Vishwavidyalaya in Uttarakhand
between September, and October 2009. The results showed that reduction in
anxiety symptoms. There was significant reduction of psychological parameter
scores after 15 days of IAPYT intervention. The percentage change of trait
anxiety was 60.42%% after Integrated Yoga Therapy. His anxiety symptoms
minimized and blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse rate came to normal
condition at the time of discharge. There was improvement in feeling of
wellness and overall functional health. This case report suggested that the
yogic lifestyle and IAPYT intervention are beneficial in treating anxiety
disorders. |
|||
|
Received 03 March 2021 Accepted 05 May 2021 Published 01 July 2021 Corresponding Author Dr.
Manoranjan Tripathy, manoranjanonly@gmail.com DOI 10.29121/jahim.v1.i1.2021.10 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2021 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Integrated Approach of Psycho & Yoga
Therapy (IAPYT), Eight State Parameters |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Psychology: Psychology is the subject by which we perform study of mind and behaviour. It may be either normal or abnormal. The branch of psychology, which deals with normal human behaviours, is known as general psychology. In addition, the one dealing with abnormal is known as abnormal psychology.
Behavior: Behaviour is the end product of brain knowledge observation nervous system physical condition, post experience virtue mind, and body in the form of thoughts action and feelings.
Abnormal Behavior: When behaviours is not usual not typical that is known as abnormal behaviours. Breakdown cognition is lead to abnormality acquiring something and adopt in day-to-day life, as known as learning when a person learns some bad things which leads abnormal behaviours is called maladaptation’s.
The term abnormal implies away from the normal, some other opinion that the term abnormal has arises from the word ANOMALOUS “ANO” means not and “Malous” stands for regular. Thus, the word abnormal implies normal. The usual characteristics, of abnormal behaviour person are: - they are self-centred punish inconsiderate unduly emotional and bad tempered antisocial etc. Now we can understand some viewpoints about abnormal behaviours.
Psychiatric Disorder: A psychiatric disorder is impairment of the nervous, causing impairment in thinking and acting. There is rather difficult definition for mental and likewise illness. In common medical understanding, mental illness is characterized by abnormal changes in thinking, feeling, memory, perceptions, and judgment, resulting in changes of talk and behaviours. Mental illness can be of different types.
Psychiatric disorders can be classified as mild and severe in nature. The milder type and most commonly concentrated psychiatric disorder are Neurosis. The severe type is the Psychosis.
Table 1
|
Table 1 Difference Between Neurosis
and Psychosis |
|
|
Neurosis |
Psychosis |
|
Minor
mental disorder |
Major
mental disorders |
|
No
hospitalization required |
Hospitalization
required. |
|
Due
to maladaptive behavior/ hereditary factor. |
Biochemical
imbalances/hereditary factor. Neurotically imbalances. |
|
Mild
to moderate impairment |
Marked
impairment |
|
Speech
& thought coherent |
Incoherent |
|
Social
group retained |
Withdrawn
delusion |
|
Preoccupation |
Delusion/Hallucinations
both |
|
Psychotherapy
required |
Medication/ECT
required |
|
Improvement
easily |
Improvement
is too late. |
Neurosis: Neurosis is a deviation in personality, but this derivation may not be an alarming nature. A neurotic person may be performing his normal duties of life. But maladjustment day to day behaviours may be seen. A neurotic person is unnecessarily sensitive and bewildered even in the normal situation of life. The neurotic person has no courage and self-confidence. Neurosis can be of different types and one of the commonest is Anxiety. Others are: -
· Anxiety Neurosis
· Phobia Neurosis
· Hypochondria Neurosis
· Hyposthenia Neurosis
· Neurasthenia
· Depressive Neurosis
· Combat Neurosis
· Pathos and Organ Neurosis
· Obsessive and Compulsive Neurosis
Anxiety Neurosis: It is one of the most commonly encountered Psychiatric Disorders. It is a functional disorder consisting of a group of minor mental disorders involving only a segment of the personality. Neurotics do not lose touch with reality and are quite able to meet the ordinary demands of everyday living. The basic and predominant features being tension, fear, and worry, but there is a general agreement that the effect of anxiety is the basic component in all type of neurosis.
Anxiety Neurosis is also known as anxiety reaction. On the basis of several investigations, it has been found that cases of Anxiety Neurosis are more common in people than other types of Neurosis. It has been estimated that 30% to 40% cases of neurotic patients are cases of anxiety.
2. CAUSES ANXIETY
· Feeling of guilt.
· Decision creating Anxiety
· Some prior painful experience
· Threat from some repressed desires
· Fear of loss of status
· Excessive use of intoxicants
· Identification with the Anxiety attitude of parents
· Defective socialization
· Indifference and lack of cordiality in family relationship
· Extra marital affaires of parents
· Child who lost one parent due to
1) Divorce
2) Conflicts
3) Natural cause
Psychosis: It is more serious psychiatric disorder than neurosis. It disintegrated the total personality. Whimsicalness in behaviour. The patient’s relationship with external world broken. He does not remember experiences of the past. His violent behaviour a threat to others. He is fit for mental hospital.
Thus, psychosis is such a sever disorder. That’s the personality of the individual is alarmingly disturbed. The powers of thinking and cognitive aspect of these behaviours also appear to be disintegrated.
3. CLASSIFICATION OF ANXIETY
Generalized Anxiety
· There is no specific reason for Anxiety.
· It is difficult to cure
· The cause of Anxiety is not visible
Specific Anxiety
· There is no specific reason for Anxiety.
· We can cure it easily.
· The cause of Anxiety is visible
It is the functional type of disorders the role of some organic factor is always there similarly, in the organic type of disorder, the role of some psychogenic or functional factor cannot be denied.
4. SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF ANXIETY
· Blood pressure rises
· Shivering all over the body
· Muscular tension or weakness
· Forgetfulness
· Insomnia
· Pain in the intestine
· General depression
· Poor concentration
· No appetite, Tremors
· Psychological Symptoms
· Apprehension
· Anxiety in Sleep and dream
· Dream of physical torture
· Feels inadequate to meet any Emergency
· Afraid of committing any mistakes
· Irritability and morbid fear
· Re-personalization
5. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA ANXIETY
· Excessive sweating
· Disturbed sleep
· Palpitation
· Lack of concentration and attention
· Restlessness, tiredness
· Rear of body and mind
· An autonomic imbalance gives to various visceral symptoms
6. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Medical Management Anxiety: -Both psychosomatic and medical treatment may be necessary. Psychosomatic treatment is more important. The patient should be told about the role of his unconscious and the fact should be impressive upon him that his Anxiety is meaningless. Desensitizing of situations causing anxiety. Tranquilizers may release the tension, courage, patience, and frustration- tolerance capacity should be developed in the patient personal interview of great utility. In case of severe attack hospitalization must.
7. DRUG THERAPY
· Anxiolytics
· Antidepressants
· Psychotherapy
On pharmacological level many drugs have proved highly effective. Although such medication may relive anxiety reactions. It cannot be replaced psychological and other therapies.
8. YOGIC MANAGEMENT
The Human body is made up five sheaths of existence of man, according to Yoga and Upanisad. The first and the grossest the physical frame that we are also familiar with is called “Annamaya Kosa”. The second subtler layer is the “Pränamaya Kosa” featured by the predominance of prana the life principle which flows through the invisible channels called Nadis. The other three sheaths are “Manomaya Kosa, Vijnanamaya Kosa & Anandamaya Kosa”.
Anandamaya Kosa is the subtlest & inner most sheath’s the sheath become ruler the freedom of operation in the living increases, the bliss associated with its also increases. While in Manomaya Kosa the creative power pre-dominates, in Vijnanamaya Kosa. It is the power to discern and discriminate. “Bliss” is embodied in Anandamaya Kosa, the highest stage of evolution in the manifested existence. It is the subtle among the five sheaths of existence.
In his journey towards the ultimate, man crosses these sheaths of existence one by one, through analysis called “Panca Kosa Viveka”.
8.1. THE SCIENCE OF ILLNESS
In Anandamaya Kosa, the man is the healthiest with a perfect harmony and balance of all his faculties. At Vijnanamaya Kosa there are movements but are canalized in the right direction. As such, it is in the Manomaya level that imbalances start, say the yoga texts. Likes and dislikes have come to play at this level. These imbalances amplify themselves resulting in mental illness called “Adhis”. At these stages, there are no symptoms at the physical level.
The Adhis (Primary diseases) are two folds, “Samanya” (Ordinary) and “Sara” the (essential). The former includes the diseases incidental to the body with the latter, the rebirth, to which all men are subject. The Samanya is normally produced during the interaction within the world. These may be termed as psychosomatic ailments. “Sara” who causes the birth of the physical body can be destroyed only by the realization of the causal states of mind and corresponding ability to live in Vijnanamaya Kosa and Anandamaya Kosas. In that sense, man transcends the cycles of birth and death.
8.2. PSYCHOSOMATIC ILLNESSES
When the mind is agitated during our interactions with the world at large and the physical body follows in its wake, this agitation causes fluctuations in the flow of Prana in the Nadis. The Prana flows in wrong paths flying from one to another without rhythm and harmony. The Nadis can no more in this condition, maintain stability and steadiness, but quiver. Due to these disturbances in the Prana and unsteadiness in the Nadis, the food does not get digested properly.
8.3. THE INTEGRATED APPROACH
There are some disturbances in the Manomaya Kosa which percolates into the physical Sheath (Anandamaya Kosa) through Pränamaya Kosa. Hence, in the treatment of these psychosomatic ailments it becomes, mandatory to work at all these levels of our existence to bring about the quickest results. The Integrated Approach consists in not only dealing with physical sheath, the relief of which could at the best be temporary (as it is happening with diseases of the psychosomatic type like Asthma, Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, etc.,) but also using techniques to operate on different sheaths of our existence, the overall health improvement is brought about.
Annamaya Kosa: - (The Physical Sheath)
Dynamic yoga practices help to reduce the physical manifestation of tremors of hands, palpitations etc. practices are to be given with fewer intervals of times and the dynamic yoga practices as such will help to drain out energy, helping the development of slower practices of pranayama and meditation successfully. The physical sheath Kriyas, physical movements and Yogacara’s are used to operate at the Annamaya Kosa level and to remove the physical symptoms of the ailments.
1) Kriyas are yogic processes described in “Hatha Yoga” to cleanse the inner organs of our body. They bring about the following: -
· Activating and revitalizing the organs.
· Toning up their function
· Desensitization
· Development of deep internal awareness
2) Physical exercises and movements: -
· Loosen the joints
· Stretch and relax the muscles
· Improve the forbearance power
· Develop stamina
3) Yogacara’s: - Yogacara’s are physical postural often imitating the natural posture of the animal meant to tranquil the mind.
Pränamaya Kosa (The Vital Sheath)
Prana is the basic life principal. Pranayama is a process for gaining control over prana. Difference between normal breathing kriyas and Pranayama are clearly depicted.
Breath in practices involving slow deep breathing keeps a person in stability of breath and the speed of breathing also reduces reciprocating at the level of mind by calming it down. Kapa Abhati lets out all the stagnations in the Prana and mind. Cooling Pranayama and Nadisudhi reduces and balances basal metabolism respectively. Through the practice of proper breathing and kriya we start operating on the Pränamaya Kosa. Thus, ailments are handled at this Pränamaya Kosa Level.
Manomaya Kosa (The Mental Sheath)
The culturing of mind is accomplished by focusing the mind (Dharana) initially and followed by relaxed dwelling of the mind on a single thought (Dhyana) for longer duration leading ultimately to super consciousness (Samadhi).
Practice which works at the level of Manomaya Kosa are Gita Chanting, Bhajan, Om Meditation, Cyclic Meditation etc. which combines body movements with deep internal awareness as to be performed after the practices of Asana and Pranayama when the mind is primed enough to held on the practices. Dharana and Dhyana are very essential as it directly slows down the speed of thinking by streamlining the thoughts in a proper channel, helping it to overcome fear by surrender to ultimately reality. To handle and gain control over the basic cause for mental agitation, we use the yoga techniques to control our emotions. A devotional session containing prayers, chants, stories, etc. help to build a congenial atmosphere to erode recognize, alternate, and dissipate the emotions.
Vijnanamaya Kosa (The Intellectual Sheath)
A basic understanding is the key to operate for Vijnanamaya Kosa. It is the redeemer of all miseries and obsessions. It is the lack of that inner “Jñana” which is responsible for many wrong habits, agitation’s etc.
We try to cultivate Vijnanamaya Kosa to overcome from anxiety and fear. Yogic counselling helps a lot in psychiatric patient, various lectures according to yoga and Satsanga also helpful Self-analysis to realize the true nature of their own i.e., blissful state. The advanced yoga technique “VISAK” is also very useful.
Anandamaya Kosa (The Blissful Sheath)
The mind emerges from the Anandamaya Kosa. It helps the persons to change his attitude of greed and deep attachments to the material possessions and enjoyment towards the realization that happiness is within, and each one of us in our casual state is “Ananda”. As a result, man’s outlook in life changes.
Happy Assembly takes the participants to the happy state of mind. By playing and mingling with others, they forget their own pain. With this ladder, one can go to bliss happiness i.e., the true nature of human being. Happy Assembly and ANAMS are useful for this.
The Aim of IAPYT is
· Relax the resistance of body and to improve immunity by Asanas, Pranayama and Kriyas.
· Relax the stresses in the body as whole.
· Develop proper psycho physiological attitude towards happiness of day-to-day life.
· Deal in the subtler level by calming down the mind by Mediation.
· Change the reactions to response towards onward happening.
· Don’t react but response.
· Don’t react but act.
· Bring a transformation in the thinking process of mind. A sick person, it cures and for healthy persons, it helps to not only maintain but also enhance normal health. It treats the root cause of the disease and eradicates the same without any side effects. It is slow process but never fail. It has no limitation.
· All the Kosas pertaining to the human body are closely connected and they are progressively and increasingly subtle – starting from gross – from Annamaya Kosa to Anandamaya Kosa.
Each Kosa has unique features & therefore requires various type of practices & technique for balancing various type of practices and technique for balancing it, like the imbalance in one effect the others, so does balancing ones, helps in balancing the others as well it gives an integrated beneficial effect.
It is a way of life in its totality with its numerous beneficial practices. When this is done, the result is a fully balanced personality totally free from diseases and negativity.
In psychiatric disorder “Stress is speed” is visibly seen at all levels of existence. The heightened level of alertness at the Background State of mind shows up as “sleeplessness”. The speed of flow of thoughts shows up as uncontrolled emotional surges at panic, unexplained fear resulting in crowding of thoughts. Lack of concentration extreme distractibility of mind. As uncultured mind with lack of control cannot take decisions and waves between many conflicts says Bhagawat Gita:
According to chapter no: - 6 verse no: -34
· “For Krishna: - The mind is very unsteady, turbulent, tenacious, and powerful; therefore, I consider it as difficult to control as the wind. (6-34)”
· But Lord Krishna concealed Arjuna that: -
· The mind is restless no doubt, and difficult to curb, Arjuna: but it can be brought under control by repeated practice. (Of meditation) and by the exercise of dispassion, son of Kunti (6-35)
· Poor capacity to memorize and retrieve is an obvious outcome of an anxious mind when this emotional speed percolates down into pranic imbalances.
· It can lead to manifestation of generalized autonomic imbalance with resultant sympathetic over activity leading to excessive sweating, decreased autonomous blood flow, increased heart rate with palpitations.
· Hence, the role of IAPYT to correct the problems at all levels. It works at different levels of existence and corrects the problems as follows.
9. CASE HISTORY
Table 2
|
Table 2 Details of
Personal |
|
|
Name |
Mr. L. Chandraswamy |
|
Age |
45yrs |
|
Sex |
Male |
|
Marital
Status |
Married |
|
Education |
B.sc |
|
Occupation |
Bank
Employee |
|
D.O.
A |
25th
–Sep-2009 |
|
D.O.
D |
10th
– Oct-2009 |
|
Diagnosis |
Anxiety
& Neurosis |
Medical History: Mr. L. Chandraswamy was admitting to Psycho Clinic, Dev Sanskriti Vishwavidyalaya with stammering, anxiety, negativity, disturbed dreams etc. In the age of 8 years, he suffered from polio. In schooling career, he had withdrawn himself from other curriculum activities because of teasing of his friends and others, and suspicious in nature. He has problem of Indigestion, Acidity, Irritability, Anger, Hopelessness-Low moods, Negativity, overall Anxious, and Brooding (thinking deeply), poor social interaction.
Table 3
|
Table 3 Personal History |
|||
|
Appetite |
Not adequate |
Sleep |
Inadequate |
|
Bowels |
Normal |
Micturation |
Normal |
|
Smoking |
Rarely |
Alcohol |
Very rarely/ Social Drunker |
Family History: His first elder brother is suffering from Insomnia and always depressed in mood. His second brother has acute anxiety and of late developed Diabetes.
10. PAST HISTORY
· Separated from family in 2004
· Polio affected left foot.
· Attempted suicide in IIIrd year B.Sc.
11. MEDICATION
|
Medication |
Quantities |
|
T.
Nitrosun (10mg) |
0-0-1 |
|
T.
Anxit/Resty (0.50mg) |
S-O-S |
|
T.
Atenol (0.50mg) |
1-0-0 |
|
T.
Azona 40mg |
0-0-1 |
|
T.
Fluboxin 50mg |
1-0-2 |
|
T.
Subex |
1-0-0 |
|
T.
Sulyon 70mg |
0-0-1 |
|
T.
Parkin |
1-0-
1 |
|
T.
Nabox 2mg |
0-0-1 |
12. STRESS HISTORY
· First week of every month, more anxiety, tension, and muscle tension.
· Lost his mother one and half years back.
· Unhappy childhood.
Investigation Available: Nothing significant.
Aim Of Present Therapy: For overall stability to improve social behaviours.
Counseling: Counsellor advised him to improve the self-confidence and change his attitude towards the situations. Work with awareness and without expectation. Try to be busy himself, cultivate his attitude and think positively. Don’t afraid by happening, be calm and discriminate the situation, also be social with people make friends, talk to peoples, and lastly advised him to emphasize more on dynamics and games which helps him to overcome his problem. And attend Lectures and Satsanga more. Counsellor suggested doing all kriyas.
Table 4
|
Table 4 Iapyt Practices with Special
Techniques for Anxiety Neurosis |
|||
|
Loosening
Exercise: |
Yogasanas: |
Pranayama: |
Meditation: |
|
Jogging
Jumping Spinal Twist Spinal Stretch Knee Stretch Backward & Forward Bending
Alternate Toe Touching IRT Suryanamaskara Relax by walking Tiger Stretch Cycling
Alternate Bhujangasana & Parvatasana PaschimotanasanaStretch Side Leg
Raising QRT |
Ardhakati
Chakrasana (each side) Ardha Chakrasana Padahastasana Bhujangasana Salabhasana
Dhanurasana Sarvangasana- Matsyasana Vakrasana Ustrasana Sasankasana Garudasana
Ardhamatsyendrasana DRT |
Kapalabhati
Sectional Breathing Chandra Anuloma Viloma CoolingPranayamas
(Sitali/Sitkari/Sadanta) Nadisuddhi Sectional breathing Bhramari KRIYA: Jala Neti Sutra Neti Vamana Dhouti |
Om
Meditation Nadanusandhana MSRT PSYCHOLOGICAL THERAPY: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) |
Table 5
|
Table 5 Daily
Routine with Attendance Data |
|||||
|
Sessions |
Duration |
Timing |
Ts |
As |
% Attendance |
|
MORNING
SESSION |
|||||
|
Om
Meditation |
5.30-6.00 |
½
Hours |
10 |
9 |
90% |
|
Kriyas |
5.30-6.00 |
½
Hours |
5 |
4 |
80% |
|
Special
Techniques |
6.00-7.00 |
1
Hours |
15 |
14 |
93.33% |
|
Pranayama |
7.00-7.30 |
½
Hours |
15 |
14 |
93.33% |
|
Nadanusandhana |
7.30-8.00 |
½
Hours |
15 |
14 |
93.33% |
|
Yog
Nidra |
8.00-8.30 |
½
Hours |
15 |
14 |
93.33% |
|
AFTERNOON
SESSION |
|||||
|
DRT |
1.00-1.30 |
½
Hours |
15 |
13 |
86.67% |
|
Parameters |
1.30-2.00 |
½
Hours |
15 |
13 |
86.67% |
|
Counseling |
2.00-3.00 |
1
Hours |
15 |
13 |
86.67% |
|
Cyclic
Meditation |
3.00-4.00 |
1
Hours |
15 |
13 |
86.67% |
|
EVENING
SESSION |
|||||
|
Trataka |
6.00-6.30 |
½
Hours |
15 |
10 |
66.67% |
|
MSRT |
6.30-7.30 |
½
Hours |
15 |
12 |
80.00% |
Graph 1
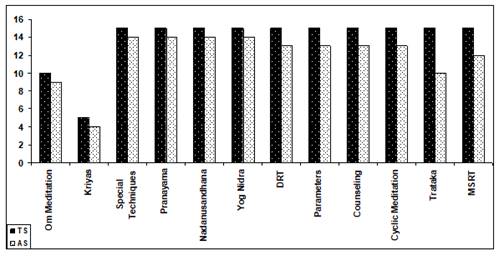
|
Graph 1 Graph of Daily
Routine with Attendance Data |
Note Below
TS – Total Sessions,
AS – Attendant Sessions
DRT – Deep Relaxation Techniques
MSRT- Mind Sound Resonance Techniques
13. PARAMETERS MEASURED AND DATA PRESENTATION
Table 6
|
Table 6 General
Parameters |
||||
|
S. N |
Particulars |
BT |
AT |
% Change |
|
1 |
BP.
Sys (mm/Hg) |
142 |
128 |
9.86% |
|
2 |
BP.
Día (mm/Hg) |
92 |
78 |
15.22% |
|
3 |
PR/min |
96 |
74 |
22.92% |
|
4 |
RR/min |
28 |
13 |
53.57% |
|
5 |
BHT
(sec) |
13 |
21 |
61.54% |
|
6 |
Weight
(Kg) |
71 |
65 |
8.45% |
Graph 2
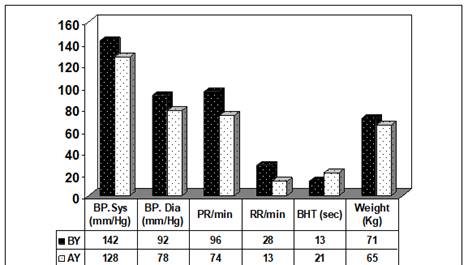
|
Graph
2
Graph of General Parameters |
Note Below
BT – Before Therapy
AT – After Therapy
PR – Pulse Rate
RR- Respiration Rate
BHT- Breath Holding Timing
Table 7
|
Table 7 Clinical
and Specific Parameters |
||||
|
S. N |
Particulars |
BT |
AT |
% Change |
|
1 |
Symptom
Score |
23 |
6 |
78.56% |
|
2 |
Medication
Score |
9 |
4 |
50% |
Graph 3
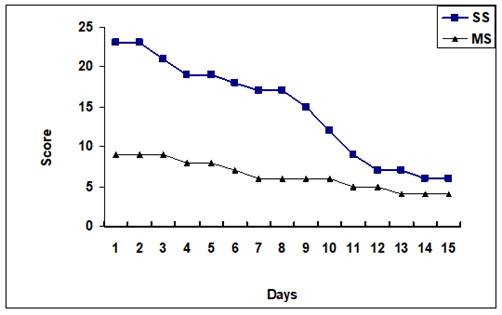
|
Graph
3
Graph of Clinical and Specific Parameters (Day by Day) |
Note Below
BT – Before Therapy
AT – After Therapy
SS - Symptom Score
MS - Medication Score
14. PSYCHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS
Table 8
|
Table 8 The Eight
State Questionnaires |
||||
|
S. N |
Particulars |
BT |
AT |
% Change |
|
1 |
Anxiety |
96% |
38% |
60.42% |
|
2 |
Stress |
94% |
42% |
55.32% |
|
3 |
Depression |
90% |
46% |
48.89% |
|
6 |
Regression |
78% |
42% |
46.15% |
|
5 |
Fatigue |
92% |
47% |
48.91% |
|
4 |
Guilt |
86% |
34% |
60.47% |
|
7 |
Extraversion |
42% |
38% |
9.52% |
|
8 |
Arousal |
86% |
42% |
51.16% |
Graph 4
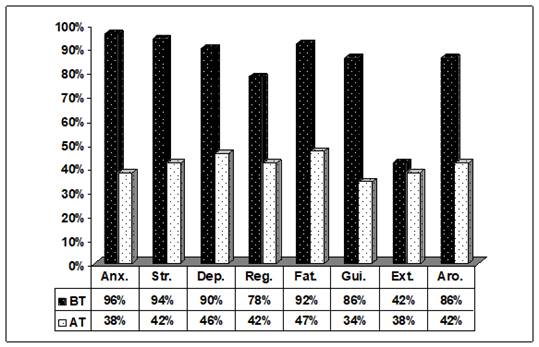
|
Graph
4
Graph of Psychological Parameters |
Note Below
BT – Before Therapy
AT – After Therapy
15. RESULTS
General Parameters
· BP- Before Therapy BP was measured 142/92 mm/Hg and After Therapy 128/78 mm/Hg with significant change of 9.86%.
· PR- Before Therapy Pulse Rate was measured 96/mint. and After Therapy 74/m with change of 22.92%.
· RR- Before Therapy Respiratory Rate was measured 28/mint. and After Therapy 21/mint. with change of 53.57%.
· BHT- Before Therapy Respiratory Breath Holding Time was measured 13sec and After Yoga 21sec with change of 61.54%.
· Wt.: - Weight was measured 71Kg Before Therapy and After Therapy 65Kg with the change of 8.45%.
Clinical and Specific Parameters
· SS - Before Therapy Symptoms Score was measured 23 and After Yoga 06 over all change of 73.91%.
· MS - Before Therapy Medication Score was measured 9 and After Therapy 4 with change of 55.56%.
Psychological Parameters
· Anxiety - Before Therapy Anxiety Score was measured 96% and After Therapy 38% significant change of 60.42%.
· Stress - Before Therapy Stress Score was measured 94% and After Therapy 42% significant change of 55.32%.
· Depression - Before Therapy Depression Score was measured 90% and After Therapy 46% significant change of 48.89%.
· Regression - Before Therapy Regression Score was measured 78% and After Therapy 42% over all change of 46.15%.
· Fatigue - Before Therapy Fatigue Score was measured 92% and After Therapy 47% over all change of 48.91%.
· Depression - Before Therapy Depression Score was measured 90% and After Therapy 46% significant change of 48.89%.
· Guilt - Before Therapy Guilt Score was measured 86% and After Therapy 34% significant change of 60.47%.
· Extraversion - Before Therapy Extraversion Score was measured 42% and After Therapy 38% change of 9.52%.
· Arousal - Before Therapy Arousal Score was measured 86% and After Therapy 42% change of 51.16%.
16. DISCUSSION
A 15 days IAPYT protocol was administered to a 45-year-old participant with anxiety disorder. There was significant reduction in trait anxiety at the time of discharge. This therapy helped him, and it was easy to adopt. The IAPYT consisting of Loosening Exercise, Yogacara’s, Pranayama, Kriya, Meditation and Relaxation Techniques helped to manage stress and reduced anxiety symptoms. It leads to physical and psychological benefits, which is discussed in Yoga Vasistha (Venkatesananda, 1985). This case gives the proper clinical evidence of the use of integrated approach of yoga therapy in anxiety disorders.
17. DECLARATION OF PATIENT CONSENT
The researchers certify that he has obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given his consent for his images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patient understands that name and initials will not be published, and due efforts will be made to conceal identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
18. CONCLUSION
From the above case it can be concluded that IAYPT helps in psychosomatic disorders, but there should be proper response patient side. During his staying he was exposing to intense IAYPT and Voice Culture along with regular counselling for which he was found co-operative. At the time of discharge, he was feeling better than earlier and noticed some change in his talk (Positivist). He has been advised to continue the Special Technique and regular follow up with the concerned doctor. IAYPT is an effective tool.
If someone practices very regularly with dedication it helps to control Anxiety. Thus, we see IAYPT is helpful for all psychosomatic ailments.
REFERENCES
Barlow, D. H. & Durand, V. M. (1995). Abnormal Psychology : An Integrated Approach. Cengage Learning.
Visser, L. D. Knaap, L. J. V. D. Loo, A. J. A. E. Weerd, C. M. M. Ohl, F. & Bos, R. V. D. (2010). Trait Anxiety Affects Decision-Making Differently In Healthy Men And Women : Towards Gender-Specific Endophenotypes Of Anxiety. Neuropsychologia, 48(6), 1598-1606.
Dhansoia, V. Bhargav, H. & Metri, K. (2015). Immediate Effect of Mind Sound Resonance Technique On State Anxiety And Cognitive Functions In Patients Suffering From Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Self-Controlled Pilot Study. International Journal Of Yoga, 8(1), 70.
Freiheit, S. R., Vye, C., Swan, R., & Cady, M. (2004). Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Anxiety : Is Dissemination Working ? The Behavior Therapist, 27(2), 25–32.
Kumar, N. & Pradhan, B. (2017). Immediate Role Of Two Yoga-Based Breathing Technique On State Anxiety In Patients Suffering From Anxiety Disorder: A Self As Control Pilot Study. International Journal Of Yoga-Philosophy, Psychology And Parapsychology, 5(1), 18.
Nagendra, H.R. (2010). Yoga Its Basis And Applications. Bangalore : Swami Vivekananda Yoga Prakashana.
Venkatesananda S. (1985). Vasistha’s Yoga. 1st Ed. New York : State University of New York Press.
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2021. All Rights Reserved.