ShodhKosh: Journal of Visual and Performing ArtsISSN (Online): 2582-7472
|
|
Evaluating the Role of AI in Visual Marketing Management
Dr. Latika Rahul Desai 1![]() , Dr. Deepali Rajendra Sale 2
, Dr. Deepali Rajendra Sale 2![]() , Dipali Manish Patil
3
, Dipali Manish Patil
3![]() , Dr. Vaishali
Vidyasagar Thorat 4
, Dr. Vaishali
Vidyasagar Thorat 4![]() , Dr. Nitin Ashok
Dawande 5
, Dr. Nitin Ashok
Dawande 5![]() , P. Malathi 6
, P. Malathi 6![]()
1 D.
Y. Patil College of Engineering, Pune, India
2 D.
Y. Patil College of Engineering, Akurdi, Pune, India
3 Pimpri Chinchwad College of
Engineering Nigdi, Pune, India
4 D Y Patil College of Engineering,
Ambi, Pune, India
5 Computer Engineering, D Y Patil
College of Engineering, Ambi, Pune, India
6 Principal, D. Y. Patil College Of Engineering, Akurdi, Pune 44, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
The design
practices on which the visual marketing management is founded have evolved
into the data-driven and analytics-based systems of decisions. The following
paper is an evaluation of the way AI will be used to radically transform the
management of visual marketing by automated analysis, creating, optimization
and controlling of visual content in online platforms. The research is
premised on the visual communication and computational intelligence theory,
and the authors present how computer vision, deep learning, and generative AI
models can assist visual marketing to generate and implement strategic
designs more effectively. It implies a fully experimental design that
involves enormous image and video files created as a result of branding and
advertising campaigns and social media promotion. It is measured in
multi-level measures which include visual effectiveness, brand consistency,
audience engagement and ROI. Empirical results of the research demonstrates that AI based visual marketing systems are much
more useful in increasing relevance of content, emotion and cross platform
compatibility of brands compared with manual systems or rule
based systems. The outcomes also indicate measurable increase in
efficacy of the campaigns, quicker design procedures, and better consistency
of the enforcement of the brand identity. |
|||
|
Received 21 June 2025 Accepted 05 October 2025 Published 28 December 2025 Corresponding Author Desai
Latika Rahul, latikadesai@gmail.com
DOI 10.29121/shodhkosh.v6.i5s.2025.6971 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Visual Marketing Management,
Computer Vision, Generative Ai, Brand Consistency |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Management of visual marketing has become a key element of the modern branding and communication practice due to blistering development of digitalization, social media, and consumer touchpoints that are visual-based. Images, videos, animations, and interactive graphics are taking over the role of brands when it comes to communications of identity, value propositions, and emotional stories. The visual elements in such a space are no longer auxiliary to the message in text and they serve as a main source of meaning, persuasion, and involvement. With the volume, velocity, and multiplicity of visual content ever-increasing, companies are increasingly challenged to design, manage, assess, and scale visual marketing assets in a more consistent and information-based fashion. Traditional means of taking care of visual marketing have largely been reliant on the ingenuity of people, understanding of designers and personal feeling. These practices are significant and are usually subjective, they can not be scaled, and their feedback is slow Ellahham et al. (2020). The visual effectiveness, brand consistency and response by the audience is more cumbersome to be measured manually when a campaign crosses the platform, regions and segments of the audience. Also, the consumer need to be personalized and have a real-time relevance only adds to the growing demand of the adaptive and intelligent visual strategy. These limitations have resulted in a necessity to possess the tools of computation that can analyze the visual information in a systematic manner, study the interaction with the audience and make successful marketing choices. Another innovative factor in this scenario, which has been introduced by artificial intelligence, is offering better sides of automating and improving visual marketing managerial tasks Allioui and Mourdi (2023). When used on visual information, AI can process a lot of visual data, desegregating semantic, aesthetic, and emotion data that would not have been easily quantifiable previously, with computer vision, deep learning, and generative modeling. The technologies enable the marketers to stop at the superficial measurements and proceed to deeper comprehension of how the visual qualities impact attention, perception and engagement Yaiprasert and Hidayanto (2023). The adoption of AI in the visual marketing processes allows organizations to shift to the reactive content assessment system to proactive and predictive system of visual strategy development.
Besides the analysis, AI is also increasingly a more present element of visual content as both a production phase and optimization. Generative models are used to produce images, layouts, and variations depending on specific audience, platforms, the optimization algorithms is dependent on visual resource optimization, and the basis of the algorithm is dependent on performance feedbacks. It can restructure the creative process in order to experiment and customize it rapidly and iterate the process without losing the strategic focus Naradda et al. (2020). At the same time, the AI-based brand management systems will assist in keeping the consistent usage of logos, colors, typography, and layouts, which is one of the long-standing problems of widespread visual marketing procedures. The implementation of AI in visual marketing management despite these developments is characterized by essential conceptual, methodological, and managerial concerns. The need to critically evaluate the effect of AI-based systems on visual performance, brand consistency, and investment efficiency, and their influence on the human creativity and strategic management also exists Tolstoy et al. (2022). The issues regarding transparency, bias, ethics design, and creative autonomy also confirm that systematic research is also significant in this field. To be responsible and effective in using AI, it is necessary to understand both the abilities and the constraints of AI. This study therefore analyses the importance of artificial intelligence in visual marketing management through the synthesis of theoretical point of view and empirical research. It discusses major AI technologies used in visual analysis, content strategy, and brand governance and evaluates its effectiveness in terms of performance, engagement, and consistency results Satar et al. (2024).
2. Theoretical Foundations of Visual Marketing and AI
2.1. Concepts and evolution of visual marketing management
The theories of visual communication, semiotics, and consumer psychology are the basis of visual marketing management since they focus on how images, symbols, colors, and space arrangements communicate meaning and then impact perception. The initial visual marketing traditions were rather design-oriented, with emphasis laid on aesthetics, brand symbolism and manual instructions on logos, typography and layouts. The brand manuals were kept in a static state and effectiveness was estimated based on post-campaign sales or the qualitative feedback of the audience was assessed. These strategies showed a linear and mostly intuitively determined perception of the role of the visuals on consumer behavior Ta’Amnha et al. (2024). As mass media and digital advertising spread, the visual marketing management took a more organized and strategic direction. The visual assets started to be managed as resources and the coordination was necessary in the print, broadcast, digital. This development was further propelled by the emergence of social media and mobile which led to a larger and wider range of visual content and how quickly audiences could consume it. Therefore, the visual marketing management has included analytics, performance measurement, and audience segmentation to make design choices Abrokwah-Larbi and Awuku-Larbi (2024). Visual marketing management is conceptualized in the modern context as a constant, data-driven process combining creative design, brand governance, and constant optimization.
2.2. Artificial Intelligence Paradigms Relevant to Marketing
Marketing-related paradigms of artificial intelligence have their origins in theories of machine learning, pattern recognition, and decision automation, and seek to allow systems to learn through data and increase their performance with time. Early AI implementations of marketing were rule-of-thumb and expert-driven, where heuristics were used to segment or target or recommend content to the user. Although they worked well in limited environments, they were not very flexible and failed to describe the intricacy of the consumer behavior and visual representation Lee and Park (2022). The development of AI paradigms that are based on data was an important theoretical change. The learning models available supervised and unsupervised allowed marketers to detect the trends in huge datasets, including customer preferences, engagement tendencies and response behavior. These paradigms aid in activities in the visual marketing such as image classification, object detection as well as clustering of visual styles in visual marketing. Deep learning, and especially neural network architectures, expanded these capabilities with features representations in a hierarchical form, which enable AI systems to perceive both low level visual features and high level meaning Tanguturi and Muley (2023). Other more recent AI paradigms put more emphasis on generative and adaptive intelligence. Table 1 shows the continuous AI developments that enhance the effectiveness of marketing the visuals and company management. Generative models allow the generation of new visual content, layouts, and variations whereas reinforcement learning allows the marketing strategy to be continuously optimized using feedback-based decision making.
Table 1
|
Table 1 Comparative Analysis of Related Work on AI in Visual Marketing Management |
||||
|
Application Domain |
AI Technique Used |
Visual Data Type |
Key Focus Area |
Limitations |
|
Digital Advertising |
CNN |
Images |
Visual appeal prediction |
Limited personalization |
|
Social Media Marketing Baabdullah et al. (2021) |
Deep CNN |
Images, Videos |
Visual sentiment analysis |
Platform-specific bias |
|
Brand Analytics |
Computer Vision |
Images |
Logo detection and branding |
No layout analysis |
|
E-commerce Gao et al. (2023) |
CNN + RNN |
Product Images |
Conversion prediction |
Static images only |
|
Video Advertising |
3D CNN |
Videos |
Viewer attention modeling |
High computational cost |
|
Visual Storytelling Alhosani and Safian (2024) |
Transformer |
Images, Text |
Narrative coherence |
Limited brand focus |
|
Brand Management |
Deep Learning |
Images |
Brand consistency checking |
No ROI linkage |
|
Personalized Marketing |
Multimodal DL |
Images, Metadata |
Visual personalization |
Privacy concerns |
|
Emotion Marketing Otto et al. (2020) |
Affective Computing |
Images, Videos |
Emotion-aware design |
Cultural sensitivity issues |
|
Creative Automation |
GAN |
Images |
Visual content generation |
Control limitations |
|
Cross-Platform Branding Liestyanti and Prawiraatmadja
(2021) |
Vision Transformers |
Images |
Visual identity consistency |
Dataset dependency |
|
Marketing Optimization |
Reinforcement Learning |
Images, Videos |
Campaign optimization |
Training complexity |
|
Visual Marketing Mgmt. Samson and Bhanugopan (2022) |
CV + DL + GenAI |
Images, Videos |
Analysis, creation,
consistency |
Requires governance and
ethics |
3. AI Technologies in Visual Marketing Management
3.1. Computer vision for image and video content analysis
The computer vision is a cornerstone technology of visual marketing management based on AI because it allows automated computer interpretation on a large scale of images and videos. It solves the problem of object, scene, face, text, color, spatial association, and positioning in visual data using computational procedures to extract information and convert the raw pixels into information, which can be analyzed. Computer vision is used in marketing to aid systematic evaluation of visual resources in advertisement creatives, social media posts, websites, and video campaign Elgendy et al. (2022). Objects detection, scene recognition, logo identification, facial expression analysis are some of the tasks that enable the marketer to know which visual features are there and whether they are featured prominently or not.
Figure 1
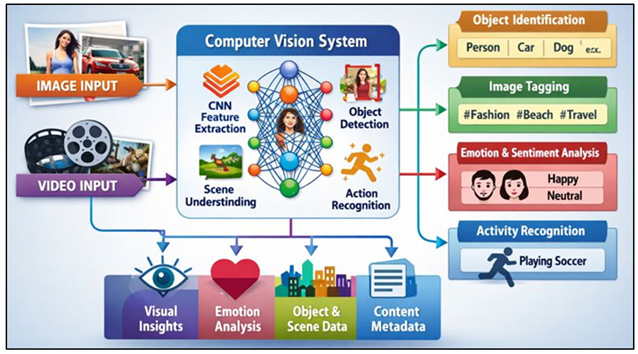
Figure 1 Architecture of Computer Vision for Image and Video
Content Analysis in Visual Marketing Management
Video content analysis goes even further in these abilities by recording time-based fluctuations, movement pattern, and frame level changes. Figure 1 demonstrates automated visual cognition that allows data-driven image and video marketing. This allows assessing the visual structures of storytelling, timing, and cues of attention in promotional videos or social media videos of a short format. A computer vision can also be used to monitor visual saliency and viewer attention, providing data about the frames or objects that stimulate attention. This kind of analysis can be seen to be in support of an evidence-based refinement of the visual narratives instead of a subjective interpretation by itself. As a manager, the computer vision would allow scaling brand compliance and content performance across platforms.
3.2. Deep Learning Models for Visual Feature Extraction
The deep learning models are instrumental in the visual marketing management as it allows deep and hierarchical visual feature extraction within the complex media content. In contrast to the common traditional methods of handcrafted descriptors, deep learning architectures are automatically trained to learn feature representations directly out of the data in a manner that reflects both low level features (color gradients, textures), and high level features (objects, styles and emotional features). This hierarchical learning ability is mostly useful in marketing conditions in which the visual meaning is subtle and contextual. Deep learning models can be used in visual marketing to perform such tasks as aesthetic quality, style recognition, sentiment, and engagement prediction. These models are capable of learning patterns using massive amounts of data of images and videos, particularly combined with information of audience interactions, to connect particular visual features with consumer reactions. This will allow marketers to analyze not only the content of the content, but also the effect of visual attributes on attention, preference, and recall. Deep models can also be used to generate feature embeddings, which can be analyzed when it comes to similarity analysis, allowing visual assets to be clustered and campaign variants to be compared. Strategically, personalization and optimization is supported by the deep learning-based feature extraction.
3.3. Generative AI for Visual Content Creation and Adaptation
The application of generative AI to visual marketing management opens a paradigm shift in visual content creation and adaptation because the visual content can be generated automatically. Instead of analysing existing materials, generative models create new images, layouts and variations of designs relying on learned patterns in large visual datasets. This will enable marketing departments to quickly generate innovative options and still stay within the brand image and strategic goals. Generative AI is used in practice to design banners automatically, create creatives on social media, create visuals of products, and design marketing visuals tailored to each user. These systems are capable of personalizing content at scale by conditioning every generation on factors like audience interests, platform specifications, promotional objectives, etc. Alteration mechanisms also enable the re-sizing, re-colouring or remodelling of the available visuals into specific channels without being manually redone. This lowers the cost and time of production and allows ongoing experiments with A/B testing and the ability to refine the product after multiple experiments. Creative workflow is another area where generative AI impacts the issue by reinventing the connection between the human designer and the intelligent systems.
4. AI-Driven Visual Content Strategy and Design
4.1. Automated visual asset generation and optimization
One of the most essential strategic uses of artificial intelligence in visual marketing management is automated generation and optimization of visual assets. Through AI-based design systems, companies are able to generate high quantities of visual assets effectively and stay on brand and campaign without sacrificing quality. Instead of using fixed design cycles, AI can be used to optimize constantly based on the real-time engagement data. Automated generation helps in quick experimentation as a strategic position. It is possible to make multiple design variants and deploy them at the same time so that the marketers can compare what visual elements (color schemes, imagery, composition, or call-to-action placement) work better in different platforms. Optimization optimization algorithms will then make adjustments to assets on iterative basis as observed results in accordance with the measurable goals like clicking through or conversion performance. This turns visual strategy into a creative choice and into an adaptive process that is based on a feedback process. Automation has a managerial effect by decreasing the bottlenecks of production and shortening the campaign timelines so that it responds faster to market trends and audience behavior.
4.2. Personalization of Visual Marketing Content
Individualization has already become a specific ideal of successful visual marketing, and AI-based systems offer the analytical and computational background needed to realize it at the necessary scale. It is possible to tailor visual content to the preferences and demographics of an individual as well as the context of use by using AI models to combine user data, behavioral signals, and contextual information to create more relevant and personalized visual content. This shifts the visual marketing strategy of one-size-fits-all design to audience-focused communication tactics. Practically, AI personalization is the act of choosing, altering, or creating visual assets that will appeal to particular groups or individuals. The visual features (imageries, color scheme, product focus and layout structure) may be dynamically changed depending on the expected preferences or interactions in the past. We can give an example of various visual stories that can be shown to the users based on their browsing history, location, or engagement pattern. Such a flexible strategy may make it more relevant and valuable, enhancing emotional engagement and brand loyalty. Strategically, customized visual marketing will boost the engagement metrics and build relationships in the long term. It also allows marketers to synchronize visual communication with customer experiences, and provides various visual information at the awareness, consideration, and conversion phases. Nevertheless, personalization should be done efficiently through appropriate data governance and transparency in order to ensure user confidence.
4.3. Emotion-Aware and Sentiment-Driven Visual Design
Sentiment-driven and emotion-sensitive visual design indicates a new level of artificial intelligence application to the visual marketing strategy which focuses on the emotional value of visual communication. Color, composition, imagery, and facial expressions are all visual elements that are critical in developing audience emotions which consequently affect attention, memory and decision making. The systems of AI can allow modeling these emotional relationships systematically through the analysis of visual features in their connection to the sentiment of the audience and behavioral reactions. Based on computer vision and affective computing, AI models can detect emotional indicators of images and videos, including mood, tone, expressive intensity. Figure 2 illustrates how emotional visual adaptation can improve the effectiveness of personalization, engagement and strategic design. Such insights enable the marketers to determine how visual materials can create desired emotional reactions like trust, excitement, or calmness.
Figure 2

Figure 2 Emotion-Aware and Sentiment-Driven Visual Design
Framework
This information is then processed by sentiment-driven design frameworks to drive content creation and adaptation to ensure the visual expression of the campaign objectives or brand positioning. Emotion-aware design is strategic and helps generate more believable and sensitive visual marketing. Campaigns may be customized to align the audience emotional conditions or situation increasing its relevance and resonance. As an example, tranquil imagery during wellness matters can be considered more important, and active styles in their promotional campaigns.
5. Experimental Design and Methodology
5.1. Dataset description and visual marketing use cases
The experimental model is based on a diverse and representative dataset which is set to reproduce the actual visual marketing situations. The data base includes image art and video material which is gathered through digital advertising campaigns, social media advertising posts, online stores, and brand communication sources. The industry coverage of the visual content includes a variety of industries, such as retail, consumer goods, technology, and services, which guarantees the wide range of findings. Different assets are provided with contextual information, including the type of platform, campaign goal, target audience segment, and time-period. To facilitate monitored and comparative analysis the dataset is combined with the engagement indicator such as impressions, click-throughs, shares, likes, and indicators of conversion. Annotations related to the brand include logo presence, color, typography, and structure. Besides, the sentiment and emotional labels are inferred by responses of the audience and textual feedback in order to provide emotion-oriented modeling. The data can be used in several cases of visual marketing. These are visual effectiveness prediction, brand compliance assessment, personalization of content and automated optimization of assets. Image datasets facilitate the analysis of the images in a static manner whereas video datasets facilitate the modeling of the temporal structure of narratives and attention patterns. The data is also split into training, validation and testing sets to avoid leakage and ensure sound assessment. This generalized data model enables to conducted systematic research of AI performance in multiple visual marketing management tasks.
5.2. Model Training, Validation, and Benchmarking
Reliability and reproducibility Model development is achieved in accordance with a structured training, validation and benchmarking protocol. Visual feature extraction, sentiment inference and performance prediction models are designed separately, which indicates the modular nature of the proposed framework. Iterative optimization methods are used to conduct the training, and hyperparameters are optimized using the search strategies of validation. Validation datasets are employed to track the dynamics of learning and to eliminate overfitting as well as to choose the best model settings. With the aim of ensuring stability and enhancing robustness, early stopping and regularization is employed. In order to measure comparative performance, the AI-based methods are compared to the traditional rule-based systems and the classical machine learning models based on the handcrafted features. The incremental value of deep learning and generative models in visual marketing situations is pointed out in this comparative analysis. The benchmarking is done on various tasks and data sets to assess consistency and scalability.
5.3. Evaluation Metrics for Visual Effectiveness and ROI
The evaluation metrics are created to address the visual communication excellence as well as the business-related results. The metrics of visual effectiveness are measured with the help of the aesthetic appeal and brand consistency, emotional alignment, and attention capture. These are color, layout, and typography similarity scores, sentiment alignment scales and visual saliency scores based on model outputs. These metrics allow objective assessment of visual assets on an objective basis as opposed to the subjective design evaluation. Measures associated with engagement give an indication of the response of the audience. The performance of visual content across platforms is measured by the standard indicators like the click-through rate, the engagement rate, the dwell time, and the frequency of sharing. These measures are examined against visual features in order to determine drivers of effectiveness. In the case of video material, temporal measures can be used to measure retention and drop-off rates of the viewer and to associate narration structure with engagement processes. One of the measures used to determine the ROI is the linkage of visual performance to conversion performance and cost efficiency. Financial impact is measured using metrics like, conversion rate uplift, cost per acquisition and incremental revenue contribution. The comparative analysis of AI-performing and non-AI workflows shows the efficiency increase and performance improvement.
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Quantitative performance improvements enabled by AI
The quantitative findings of the experiment proved significant increases in performance in visual marketing due to AI-based approaches. Relative to the conventional knowledge rule-based and manual design workflow, AI-based systems were more successful in visual effectiveness prediction and engagement forecasting. The use of automated optimization resulted in quantifiable increases in the click-through rate, conversion rate and audience retention in image campaigns and video campaigns. Personalization based on features also increased relevance and led to an increase in platform interaction rates. Moreover, AI-driven content creation also saved time on content production and relied on visual quality or was even better. The results of performance benchmarking show that deep learning and generative models were always superior to the traditional methods in predictive reliability and scalability.
Table 2
|
Table 2 Comparative Performance Metrics – Traditional Vs. AI-Driven Visual Marketing |
|||
|
Performance Metric |
Traditional Approach (%) |
AI-Driven Approach (%) |
Improvement (%) |
|
Visual Effectiveness
Prediction Accuracy |
72.4 |
89.6 |
17.2 |
|
Click-Through Rate (CTR) |
2.85 |
4.62 |
62.1 |
|
Conversion Rate |
1.94 |
3.28 |
69.1 |
|
Engagement Rate |
6.8 |
11.5 |
69.1 |
|
Audience Retention (Video) |
54.3 |
73.9 |
19.6 |
Table 2 demonstrates a vivid contrast between the conventional visual marketing strategies and AI-driven methodologies and thus shows that there are consistent improvements in performance in all the measures considered. Click-through rate is the most remarkable as 2.85% goes to 4.62, which means that AI-focused visuals are much more effective in drawing the attention of users. Figure 3 demonstrates that AI-based marketing is always more effective than the traditional one in terms of the key performance indicators.
Figure 3
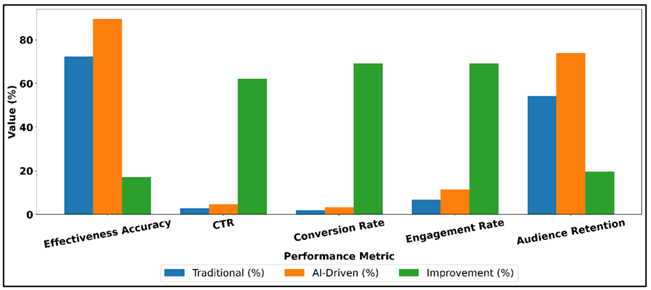
Figure 3 AI Vs Traditional Marketing Performance – Bar
Comparison
In the same way, conversion rate increases by 69.1% which proves that AI does not only attract users but also enhances the similarity of decision between visual content and consumer intent. Such an engagement rate demonstrates a similar boost, and the interaction of the viewers with AI-driven visual designs based on personalization and data-driven optimization is higher.
Figure 4

Figure 4 AI-Driven Marketing Performance Trends
The next part is the upgrades in visual effectiveness prediction accuracy, which indicate that AI models give more confident evaluations of the way the visuals will fare before being put into practice and less uncertainty is generated in creative decision-making. AI-based marketing performance, as demonstrated in Figure 4, is steadily rising in terms of campaigns and engagement indicator. Also, the greater viewership retention of video content presents the capability of AI to streamline visual narrative, rhythm and emotional response with time.
6.2. Impact of AI on Brand Consistency and Engagement
The adoption of AI was especially significant in terms of visual marketing campaign brand consistency and interactivity. The brand compliance systems which were automated minimized disparities in the application of logos, color and the structure of layouts and resulted in more consistent brand expression on channels. The scores on consistency were significantly better when the AI-based monitoring was implemented continuously instead of periodically as the case of manual audits. This improved the metrics of engagement, as viewers reacted more positively towards visually consistent and familiar brand stories. Individual and emotion-sensitive visual designs also enhanced the interaction of the user, enhancing the dwell time and content sharing. The findings indicate that AI-based brand governance is strongly related to engagement performance. All in all, the consistency management that AI facilitates can not only safeguard the brand integrity, but also enhance the success of marketing by strengthening trust, recognition, and emotional bond between audiences and the marketing campaign.
Table 3
|
Table 3 Brand Consistency and Engagement Outcomes with AI Integration |
|||
|
Metric |
Without AI (%) |
With AI (%) |
Gain (%) |
|
Brand Consistency Score |
74.8 |
92.1 |
17.3 |
|
Logo Usage Compliance |
81.2 |
96.4 |
15.2 |
|
Color Palette Consistency |
78.6 |
94.7 |
16.1 |
|
Typography Compliance |
76.9 |
93.3 |
16.4 |
|
Cross-Platform Visual
Consistency |
71.5 |
90.6 |
19.1 |
Table 3 shows how the use of AI has affected brand consistency and visual congruency in the marketing channels. The percentage of brand consistency also goes up to 74.8 per cent and to 92.1 per cent which means that AI-based monitoring and compliance systems greatly enhance visual brand guideline compliance. Figure 5 indicates that AI systems have a high level of brand consistency compared to non-AI strategies. The increase in the compliance of logo use and typography compliance show how automated checking and correction systems are effective in ensuring the visual representation of the elements is standardized.
Figure 5
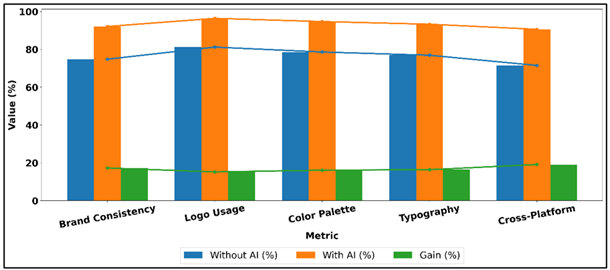
Figure 5 Brand Consistency Performance Comparison (AI Vs Non-AI)
The development of consistency in the use of color palette reveals the capability of the AI to analyze and implement the use of particular colors correctly and minimize the occurrence of unintentional deviations in the creation of artistic works. It is interesting to note that the most significant improvement belongs to cross-platform visual consistency, which is the ability of AI to align the brand image with lots of different environments with different format restrictions.
7. Conclusion
This study evaluated the importance of the use of artificial intelligence in visual marketing management based on the value of artificial intelligence in fighting the complexity, scale, and performance demands of the present digital marketing environment. Making a synthesis of the theoretical approach with empirical studies, the study demonstrates that the visual marketing can be taken out of design that is based on intuition to systematic, data-driven and adaptive models of decisions with the help of AI technologies. The design of deep learning, computer vision, and generative AI is to get into resort to automated visual content analysis, creation, optimization, and control, which transform the way companies undertake visual communication in various platforms. The AI-based systems have quantifiable visual effectiveness, engagement and operational efficiency gains in the findings. Generation and optimization of assets is a process that is carried out automatically, accelerating the creative process and to a large extent guaranteeing that the experimentation and optimization can take place as time passes. Engagement and emotion appeal through relevance and emotion-sensitive design by personalizing the content can be employed in order to enhance engagement and emotion appeal in the audience, which enhances the influence and interest of the campaign. It is interesting to note that AI brand consistency systems provide scalable alternatives to the implementation of visual identity requirements, reduction of inconsistency, and consistent brand narratives in decentralized marketing systems. Besides performance advantages, the study also indicates some of the strategic implications of AI on the visual marketing management. Creative work is not taken away by intelligent systems but rather the design and the marketing job is revisited and presented as the designer and the marketer as the one who is the strategist, curator and evaluator of the intelligent system. It is a partnership between humans and AI that permits creative freedom and managerial authority to adjust artistic expression with information.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Abrokwah-Larbi, K., and Awuku-Larbi, Y. (2024). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Marketing on the Performance of Business Organizations: Evidence from SMEs in an Emerging Economy. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 16(5), 1090–1117. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEEE-07-2022-0207
Alhosani, S. E. E. S., and Safian, E. E. M. (2024). Framework of the Mediation Effect of Artificial Intelligence Usage on the Relationship Between Innovation Factors and Organisational Performance. International Journal of Sustainable Construction Engineering and Technology, 15(2), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.30880/ijscet.2024.15.02.015
Allioui, H., and Mourdi, Y. (2023). Unleashing the Potential of AI: Investigating Cutting-Edge Technologies That are Transforming Businesses. International Journal of Computer Engineering and Data Science, 3(1), 1–12.
Baabdullah, A. M., Alalwan, A. A., Slade, E. L., Raman, R., and Khatatneh, K. F. (2021). SMEs and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Antecedents and Consequences of Ai-Based B2B Practices. Industrial Marketing Management, 98, 255–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2021.09.003
Elgendy, N., Elragal, A., and Päivärinta, T. (2022). DECAS: A Modern Data-Driven Decision Theory for Big Data and Analytics. Journal of Decision Systems, 31(4), 337–373.
Ellahham, S., Ellahham, N., and Simsekler, M. C. E. (2020). Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Health Care Safety Context: Opportunities and Challenges. American Journal of Medical Quality, 35(5), 341–348. https://doi.org/10.1177/1062860619878515
Gao, L., Li, G., Tsai, F., Gao, C., Zhu, M., and Qu, X. (2023). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Stimuli on Customer Engagement and Value Co-Creation: The Moderating Role of Customer Ability Readiness. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 17(3), 317–333. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-10-2021-0260
Lee, J., and Park, C. (2022). Customer Engagement on Social Media, Brand Equity and Financial Performance: A Comparison of the US and Korea. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 34(3), 454–474. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-09-2020-0689
Liestyanti, A., and Prawiraatmadja, W. (2021). Service Quality in the Public Service: A Combination of SERVQUAL and Importance–Performance Analysis. Journal of International Conference Proceedings, 4(3), 320–331. https://doi.org/10.32535/jicp.v4i3.1323
Naradda Gamage, S. K., Ekanayake, E., Abeyrathne, G., Prasanna, R., Jayasundara, J., and Rajapakshe, P. (2020). A Review of Global Challenges and Survival Strategies of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Economies, 8(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies8040079
Otto, A. S., Szymanski, D. M., and Varadarajan, R. (2020). Customer Satisfaction and Firm Performance: Insights from Over a Quarter Century of Empirical Research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48(3), 543–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-00657-7
Samson, K., and Bhanugopan, R. (2022). Strategic Human Capital Analytics and Organisation Performance: The Mediating Effects of Managerial Decision-Making. Journal of Business Research, 144, 637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.044
Satar, M., Alharthi, S., Asad, M., Alenazy, A., and Asif, M. U. (2024). The Moderating Role of Entrepreneurial Networking Between Entrepreneurial Alertness and the Success of Entrepreneurial Firms. Sustainability, 16(11), 4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114535
Ta’Amnha, M. A., Al-Qudah, S., Asad, M., Magableh, I. K., and Riyadh, H. A. (2024). Moderating Role of Technological Turbulence Between Green Product Innovation, Green Process Innovation and Performance of SMEs. Discover Sustainability, 5, 324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-024-00522-w
Tanguturi, R. N. V., and Muley, A. A. (2023). Enhancing Financial Institution Operations Through Data-Driven Decision-Making. Journal of Namibian Studies: History, Politics, Culture, 39, 272–282.
Tolstoy, D., Nordman, E. R., and Vu, U. (2022). The Indirect Effect of Online Marketing Capabilities on the International Performance of E-Commerce SMEs. International Business Review, 31(2), 101946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101946
Yaiprasert, C., and Hidayanto, A. N. (2023). Ai-Driven Ensemble Three Machine Learning to Enhance Digital Marketing Strategies in the Food Delivery Business. Intelligent Systems with Applications, 18, 200235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswa.2023.200235
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhKosh 2025. All Rights Reserved.

