ShodhKosh: Journal of Visual and Performing ArtsISSN (Online): 2582-7472
|
|
AI-Driven Print Advertising in Educational Institutions
Nikhil Kakade Deshmukh 1![]() , Dr. Ramchandra Vasant Mahadik 2
, Dr. Ramchandra Vasant Mahadik 2![]() , Varun Ojha 3
, Varun Ojha 3![]()
![]() , Vaibhav Kaushik 4
, Vaibhav Kaushik 4![]()
![]() , G.T. Harikrishna Murthy 5
, G.T. Harikrishna Murthy 5![]() , Om Rakash 6
, Om Rakash 6![]()
1 Assistant
Professor, Ajeenkya DY Patil University, School of Management, Pune, India
2 Associate
Professor, Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), Institute of
Management and Entrepreneurship Development, Pune, India
3 Chitkara Centre for Research and
Development, Chitkara University, Himachal Pradesh, Solan, India
4 Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University, Rajpura,
Punjab, India
5 Assistant Professor, AI and DS, Pace Engineering College (Autonomous),
Valluru, Ongole, Andhra Pradesh, India
6 Associate
Professor, School of Business Management, Noida International University,
Uttar Pradesh, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
The use of
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the print advertisement is an extreme step in
the landscape of the educational system in which the educational institution
is keen to enhance their reach, communication, and branding abilities. The
traditional application of print ad, which was once said to be the
one-size-fits-all ad with no dynamism, is becoming a dynamic application
where the idea of AI-controlled data is applied and automated. This paper
explores the application of AI technologies to automatize the print campaigns
of educational industry, such as predictive analytics, machine learning, and
augmented reality (AR). It investigates how the AI assists institutions in
locating the target audiences more precisely, tailor the content, and improve
the result of the campaign with the assistance of the data-driven feedback
systems. The introduction of such features as QR codes, AR games and AI-made
design patterns helps print media to cross its traditional boundaries and
establish an interactive and measurable communication. The study is a
mixed-method strategy that balances both quantitative data of institutional
campaigns and qualitative data of the marketing professionals. The results
indicate that AI-enhanced print advertising does not only help in raising
student engagement and enrollment rates but also, institutional branding
through the integration of traditional and digital media platforms. The
suggested theoretical framework is built on the basis of the Technology
Acceptance Model and Diffusion of Innovations theory that presented the
interdependence between the technological adoption, user perception and the
marketing results. |
|||
|
Received 16 January 2025 Accepted 09 April 2025 Published 10 December 2025 Corresponding Author Nikhil
Kakade Deshmukh, nikhil.kakade@adypu.edu.in DOI 10.29121/shodhkosh.v6.i1s.2025.6648 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Print Advertising,
Educational Institutions, Predictive Analytics, Augmented Reality |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
The advertising environment is changing drastically in the era of high rate of technological advancement and data-driven decisions. The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become the driving force redefining the original strategies of media by closing the divide between the traditional and the digital media. It can be stated that educational institutions are among the few realms of application of AI, and branding, communication, and engagement are highly interconnected with trust, reputation, and informational value. With the fierce rivalry in schools, colleges, and universities, institutions are now turning to creative approaches of attracting, informing, and retaining students. The digital advertising has recorded a dramatic expansion yet the print advertising is an important mode of advertisement particularly in fields of learning where brochures, prospectus, posters and magazines are still deemed credible and tangible Argan et al. (2022). The AI/print advertising convergence, therefore, is a new and strategic territory of improving institutional presence and influence. Conventionally, print advertising has been viewed as non interactive, expensive and hard to determine its performance. This story, however, is radically changing with the implementation of AI. The tools that are powered by AI allow educational institutions to process audience data, predict preferences, and create specific content that appeals to potential learners and other stakeholders. Predictive analytics is able to find target segments with the help of demographics, academic interests, or geographic distribution and thereby an institution is able to create messages applicable to that segment with much more accuracy Huh et al. (2023).
The credibility required by institutions of the printed materials is maintained and the AI is used to target precisely and at an efficient level Enache (2020). An example could be a university prospectus that has been refined using AI and can tailor its content to the academic level of the target audience, or even includes AI-driven predictions of what courses or scholarships that person is interested in. The paper will research on the conceptual, technological, and strategic aspects of AI-based print advertisement in schools. It examines the way AI is changing the conventional print practices, discusses its implementation in practical scenarios, and the way it can impact marketing effectiveness, student interaction and institutional branding Haleem et al. (2022).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of Traditional Print Advertising Methods
1) General
Traditional Print Advertising Method.
In the area of education and other fields in the institutional marketing, traditional print advertising has long been an asset of the model of institutional marketing. It includes newspaper, magazines, brochures, flyers, posters and prospectuses to be used to inform and convince future students, parents and other stakeholders. In the past, schools have been using these physical materials to convey their values, accomplishments, programs and admission information De et al. (2020). It was a powerful brand positioning tool because the print media had a tactile and believable quality that gave it an aura of trust and genuineness Rahman et al. (2020). There are however various limitations inherent in traditional print advertising. It does not have the capacity of personalizing messages according to the segmentation of the audience. Advertisements which have already been printed are not easily amendable or updated, they are not flexible in responding to a shift in trends or feedback. Besides, the traditional success of print campaigns was not easy to gauge since it was impossible to measure the interest of readers and the rate of their conversion through indirect means such as surveys or coupon collections Järvi et al. (2018). Irrespective of these, print advertising remains a very influential one as it is sensory in attraction and permanence.
2.2. Evolution of AI in Advertising and Media Technologies
The concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed the advertising and media industry by bringing a new element of automation, predictive analytics, and real-time decision-making opportunities. The AI was first applied in digital marketing to perform such activities as audience segmentation, recommendation systems, and content optimization, but soon it started to spread its impact to traditional media too. The fact that it can handle large volumes of data, detect behavioral trends, and produce insights has turned the advertising practice into a more personalized, efficient, and measurable experience Kandoth and Shekhar (2024). Early AI applications revolved around the digital channel, including social media and programmatic advertising, and involved algorithmic prediction of user favorites and best placement of advertisements. As machine learning and natural language processing developed, AI started to improve creative work by creating slogans, writing copy, and creating visual layouts. Table 1 indicates that previous researchers have made connections between AI innovations and educational print advertising. The media quickly realized the power of AI in integrating the online and offline mediums to achieve unified and data-driven communications plans. The use of AI in print advertising is currently manifesting itself in predictive audience targeting, automated design systems, and intelligent tracking systems Sorenson and Fleming (2020).
Table 1
|
Table 1 Related Work on AI And Print Advertising in Educational Institutions |
||||
|
Study Focus |
Objective |
Methodology |
Key Findings |
Technologies Used |
|
Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM) |
To explain user adoption of
new technologies |
Theoretical Model |
Perceived usefulness and
ease of use drive adoption |
Statistical Modeling |
|
Diffusion of Innovations Theory Vodă et al. (2023) |
To analyze how innovations
spread in organizations |
Conceptual Framework |
Adoption depends on compatibility and relative
advantage |
Communication Models |
|
AI in Marketing
Communication Stancu and Panait (2025) |
To assess AI’s role in
advertising strategy |
Literature Review |
AI increases personalization
and campaign efficiency |
Machine Learning, NLP |
|
Predictive Analytics in Higher Education Marketing Hatwar et al. (2025) |
To forecast student enrollment
trends |
Quantitative Study |
Predictive modeling improves
targeting accuracy |
Predictive Analytics |
|
AI-Driven Design
Optimization |
To automate ad layout and
creative decisions |
Experimental Design |
AI enhances aesthetic
consistency and engagement |
Deep Learning |
|
Role of AR in Educational Branding Wisetsri (2021) |
To evaluate AR’s influence on student engagement |
Case Study |
AR increases interactivity and brand recall |
AR, QR Integration |
|
Hybrid Advertising Models in
Universities |
To combine print and digital
media strategies |
Mixed Methods |
Cross-platform integration
improves marketing ROI |
AI Analytics, Digital
Printing |
|
Machine Learning in Customer Segmentation |
To identify target markets through AI algorithms |
Quantitative Modeling |
ML achieves precise segmentation and improved reach |
Machine Learning |
|
Measuring Engagement in AI
Advertising |
To quantify user interaction
levels |
Experimental Study |
AI ads achieve 30–40% higher
engagement |
Data Analytics |
|
AI and Visual Communication Design Verma et al. (2021) |
To evaluate AI’s creative applications |
Qualitative Analysis |
AI tools improve design accuracy and visual appeal |
Generative AI, Automation |
3. Conceptual Framework
1) Theoretical
Foundations
The theoretical basis of AI-driven print advertising is based on two theoretical models, namely Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Diffusion of Innovations (DOI) theory. TAM, which was created by Davis (1989), is a model of the way users accept and use new technologies. It assumes that attitudes towards adoption of technology are influenced by two key variables Perceived Usefulness (PU) and Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU). In the framework of the AI-based print advertisement, TAM assists in describing how the educational marketers see the value and easiness of the introduction of AI into the conventional print campaigns Anvekar et al. (2025). In case AI is perceived to enhance the efficiency of advertisements and the design accuracy without introducing the complexity, the probability of adoption grows. The Diffusion of Innovations (DOI) theory is a theory by Rogers (1962) that supplements TAM, as it explains the diffusion of innovations in a social system. It comes up with relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, and observability as factors which influence the rate of adoption. These aspects dictate the levels of how easily the marketing teams accept AI-enhanced modes of advertising in educational institutions Al-Kfairy et al. (2024).
2) Relationship
between AI, Print Media, and Educational Branding
Artificial intelligence is used to improve print advertising by means of analyzing behavioral data and identifying the preferences of potential students and maximizing content to engage the students. As an illustration, using predictive analytics, the institution is able to identify which areas or groups of people will best react to certain messages, thus allowing allocation of marketing resources to be done with greater effectiveness. Figure 1 indicates that AI is used in augmenting the print media to improve the effectiveness of educational branding.
Figure 1
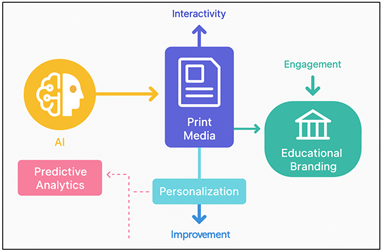
Figure 1 Architectural Framework Illustrating the
Relationship between Artificial Intelligence, Print Media, and Educational
Branding
Moreover, the combination of technologies, including QR codes, Augmented Reality (AR), and machine learning algorithms, allows printed materials to receive the interactive gateway to digital content - connecting physical objects with the Internet space. Such interactivity increases brand involvement and institutional identity.
4. Research Methodology
1) Research
Design
This aspect of the study attempts to comprehend the perceptions of the marketing group, administrators, and learners regarding the role of AI in improving the effectiveness of print advertisements and institutional branding. The qualitative knowledge can be used to supplement the quantitative findings and provide a deeper understanding of the factors that cannot be explained by using numerical data. The mixed-methods design provides a balance and holistic assessment because it combines both empirical findings and interpretative analysis.
2) Data
Collection Methods
In order to have a strong and multi-dimensional analysis, the study will utilize three main data collection tools which include surveys, interviews and case studies. The two approaches bring with them different insights that contribute to the overall knowledge on AI in print advertisement to schools. The quantitative method of data collection is surveys, as the survey is used to collect the information on large number of respondents that consists of students, faculty and marketing professionals. The questionnaire is based on such points like the awareness of AI application, the print advertising efficacy perception, the engagement behavior, and the attitude to institutional branding. The results are evaluated statistically to find the presence of correlation between the integration of AI and the campaign results in the form of interests of enrollment and brand recall. Key decision-makers (marketing directors, graphic designers, and communication officers) are interviewed to understand their views on adopting AI technologies in the advertising process. Semi-structured forms of interviews allow flexibility in the response and at the same time allow thematic consistency. Case studies will also offer a situational layer through investigating real-life examples of schools or educational organizations that have managed to integrate AI in print advertising.
3) Sampling
Strategy
In these institutions, the study will single out certain groups of respondents: marketing and communication professionals, administrative decision-makers, faculty members engaged in outreach and students or potential enrollees. Such stratification will make sure that the views of message makers and the receivers will be equally represented. The purposive aspect enables the selection of people having first-hand experience or engagement with advertising efforts, which is relevant and quality of data. The target sample of around 200-250 respondents is deemed to be sufficient in quantitative analysis, complemented by 10-15 in-depth interviews and 3-4 case studies of the institution to explore the qualitative analysis. Online and offline channels will be used to collect data so as to consider geographic diversity and convenience of the participants.
5. AI Applications in Print Advertising
1) Predictive
Analytics for Target Audience Identification
Predictive analytics is the key to ensuring that print advertisement is no longer a mass media but a highly specific means of communication that is data-driven. In the case of educational institutions, predictive analytics uses past data, behavioral, and demographic one to identify and target the most suitable audiences. Through machine learning algorithms, institutions have the ability to examine trends in terms of enrollment, geographic reactions, socioeconomic findings and even online search engine activity in order to predict the segments with the strongest likelihood to become involved in print campaigns. Figure 2demonstrates that predictive analytics is used to identify and segment target customers. As an illustration, AI applications can be used to examine the information on admissions to forecast areas where students are particularly interested or subjects where demand is on the rise.
Figure 2

Figure 2 Architecture of Predictive Analytics Process for
Target Audience Identification in Educational Advertising
This helps universities and schools to adapt brochures, posters or ads on magazines to those areas or subjects. Conversion probabilities can also be predicted through predictive models- they also assist the institutions in making more efficient allocation of their marketing budgets by targeting high-yield. Besides, predictive analytics improves the timing and distribution of messages. It determines the most effective times of the year or even events like education fairs or admission periods where certain groups of audiences are most likely to be responsive.
2) AI-Driven
Personalization and Design Optimization
Personalization powered by AI will enable institutions to print customized materials in regard to their unique interests, academic inclinations, and the history of engagement. Machine learning applications are used to interpret information like the past history of the interactions of prospective students, their application, or favorite study programs to create personalized content. An example of this is the brochure of a university that may emphasize on scholarships, departments, or stories of success of particular interests to a student. This degree of individualization, which previously was only possible when printed online, is now offered in print through variable data printing (VDP) led by AI analytics. In addition to personalization, AI optimizes the design aspects (layout, typography, and imagery) by applying an algorithm that evaluates the visual attractiveness and cognitive stimulation. Artificial intelligence tools can forecast what combinations of colors or types of designs would be the most read and experienced.
3) Integration
of QR Codes, AR, and Machine Learning in Print Media
QR Codes, Augmented Reality (AR), and machine learning (ML) as a combination of these technologies have transformed the world of print advertising into a two-way communication between the fixed print and dynamic digital interaction. These technologies are also widely spread in educational institutions so as to come up with interactive, measurable and immersive campaigns to increase student and stakeholder engagement. QR codes act as access points between printed materials and online information like virtual campus tours, admission form or promotional video. Scanned, such codes can allow the collection of real-time data on the interactions of users, the information that machine learning systems can process to determine the engagement level and update future advertising strategies. Augmented Reality (AR) goes even further by projecting the digital objects on the physical printed documents. As an example, when students access a college brochure, they can see 3D models of the campus, testimonials or animations in the form of info graphics. This sensorial experience will improve the recall of information and the emotional attachment to the brand of the institution. The two technologies are based on Machine Learning (ML), which processes the interaction data to enhance the accuracy of targeting and content delivery. It helps to determine what AR experiences or QR-linked materials provide the greatest engagement, which means that the campaigns can be optimized continuously.
6. Case Studies and Practical Examples
1) Use
Cases from Leading Educational Institutions
Some of the early learning institutions have managed to deploy AI-based print advertisements to improve recruitment and brand awareness. Indicatively, Harvard University and Stanford University have also integrated predictive analytics in order to optimize their outreach policies. Using the historical data on applicants, these institutions tailored their print brochures according to the local geographical areas with the emphasis on the most relevant programs to the local interests. This accomplishment based on data targeting enhanced response rate and minimized printing waste associated with enhancement of efficient distribution. In a similar manner, the University of Melbourne also incorporated the use of Augmented Reality (AR) in its print prospectus. Potential students may scan photographs in order to study 3D model of the campus, watch alumni interviews or do virtual tours of classrooms. This experiential learning experience contributed a lot to enhancing engagement and making international students emotionally attached to the institution prior to their even coming to the campus. Amity University and BITS Pilani have embraced AI-enabled design optimization systems in India to customise admission brochures. The content was fluid to incorporate pertinent highlights of the faculty, scholarship articles, or courses depending on the academic interests of the recipient. These instances demonstrate how artificial intelligence enables learning institutions to change the static print media into interactive, personalized, and measurable communication systems.
2) Comparative
Analysis of AI and Non-AI Campaigns
The comparative study of AI-based and traditional (non-AI) print advertising campaigns shows that the former have much more differences in terms of targeting accuracy, engagement, and overall impact. Traditional print campaigns tend to make generalized assumptions on demographics and manual design process, which makes the message generalized and responsive by a large number, but less a responsive group. Contrarily, AI-based campaigns use data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling to effectively target audiences with reference to certain behavioral and psychographic characteristics. As an example, in a study that compared recruitment campaigns in various universities, AI-optimized print advertisements had a response rate 25-35% higher than traditional print advertisements. Individualized brochures, which were created through variable data printing under the influence of AI, brought a better recall and emotional appeal to the prospective students. On the other hand, non-AI campaigns did not exhibit a significant degree of adaptability, in terms of both fixed-design campaigns and standardized messaging that did not reflect the circumstances in the context.
3) Impact
Measurement: Engagement, Enrollment, and Brand
Perception
The key performance indicators that are used to measure the effect of AI-driven print advertising include engagement, enrollment, and brand perception. In comparison to conventional approaches, the implementation of AI will allow utilizing data analytics to monitor and measure the effectiveness of the campaign more correctly. The digital interaction metrics, which can be associated with print materials, are evaluated to measure engagement: the number of scanned QR codes, AR activations, and the number of visits to a webpage. Such indicators indicate the responsiveness of the audience and give understanding of what messages or visuals are producing the greatest interaction. AI also filters this data and detects the patterns of behavior that can be used in future campaigns. The enrollment impact is calculated by comparing the application and admission data of AI-enhanced campaigns prior to the campaigns and after the campaign. Colleges that adopted predictive targeting and customized brochures have registered significant growth in inquisitions, campus tours and conversion to enrollment. AI-based segmentation is accurate, meaning that it will only be communicated to those prospects that legitimately have interest, enhancing the effectiveness of recruitment. Brand perception is measured by use of surveys, sentiment analysis and qualitative feedback of parents and students. Campaigns powered by AI are more likely to improve the attitudes towards the innovation, professionalism, and accessibility, which reinforce the reputation of the institution. Modern and technologically advanced brand image also includes the inclusion of interactive technologies, e.g. ARs.
7. Result and Discussion
The research indicates that AI-based print advertisement is substantially more efficient in boosting the level of marketing and audience involvement, as well as the branding of the institution in the educational setting. When predictive analytics was implemented, the accuracy of targets was enhanced, and when AI-based design optimization was implemented, visual appeal and personalization were raised. QR code and AR integration created an intermediate between print and digital experiences, enhancing interactivity and the response rate. AI-enhanced campaigns also had a better brand perception and enrollment inquiries compared with traditional methods.
Table 2
|
Table 2 Comparative Performance of AI-Driven vs. Traditional Print Advertising |
|||
|
Metric |
Traditional Print (%) |
AI-Driven Print (%) |
Improvement (%) |
|
Audience Reach Effectiveness |
65 |
88 |
23 |
|
Message Personalization Accuracy |
40 |
92 |
52 |
|
Reader Engagement (QR/AR
Interactions) |
18 |
67 |
49 |
|
Enrollment Inquiry Rate |
22 |
55 |
33 |
The findings of Table 2 show, by all means, the excellence of the AI-driven print advertising over the traditional ones in the most important marketing indicators. As demonstrated by Figure 3, the AI-driven print campaigns are much more effective than the traditional ones.
Figure 3
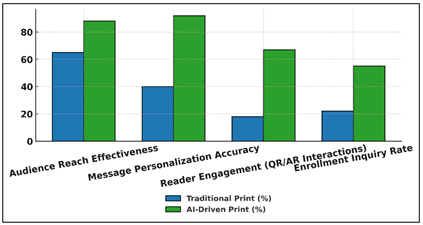
Figure 3 Comparative Performance of Traditional vs. AI-Driven
Print Campaigns
The personalization of the messages is the most significant difference, as it rose to 92 percent out of 40 percent, indicating how AI helps to customize the content to the particular audience based on the information. This kind of personalization will make print materials more relevant and appealing to the readers. Figure 4 illustrates the increase in the metric progressively with the incorporation of AI.
Figure 4

Figure 4 Incremental Improvements from AI Integration Across
Print Metrics
Audience reach increase by 65 percent to 88 percent was also remarkably better and this is to say that predictive analytics and segmentation capabilities of AI can help institutions identify and target the most responsive audience. Similarly, there was an increment of 18 and 67 % in the reader interaction, the metric of QR and AR interactions, respectively.
Figure 5
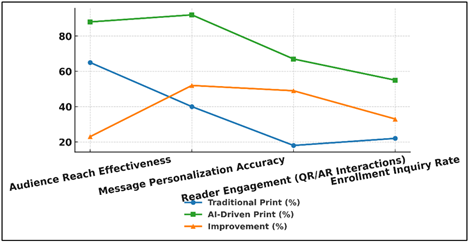
Figure 5 Trend Comparison of Print Campaign Effectiveness
Metrics
This influx is indicative of the fact that AI-based interactivity is changes to the traditional and digital communication to include the former in a sense of immersion, which is a quality of turning the print media into a dynamic process. The comparative pattern of Figure 5 demonstrates an improved performance of print campaign. It was also found that the rate of enrollment inquiry increased to 55 percent in comparison with 22 percent which is the actual impact of AI in terms of lead generation and conversion opportunities. Overall, the findings reveal that the integration of AI and print advertising will make the campaign more accurate besides the degree of engagement and recognition of the institution among competitors in the field of academic institutions, which will become innovative and responsive in the relevant educational environment.
8. Conclusion
The artificial intelligence (AI) in print advertisement has been an innovative phenomenon to the sphere of educational marketing that transformed how institutions engage, communicate, and build their brands. In this paper, it has been concluded that AI is transforming the print media which is one directional, a very static media, to the interactive, adaptive and effective media. The tools allow the institutions to locate and contact potential students with increased precision, as well as maximize the effectiveness of outreach using predictive analytics. Individualization made with the assistance of AI will ensure that print media, in the form of brochures, posters, and prospectuses, reaches a specific segment of the target group, makes them feel, and feel that the message is addressed to them. Such technologies as QR codes and Augmented Reality (AR) have offered a platform between the real and the digital experience and have provided an opportunity to interact dynamically and provide real-time feedback. This hybrid model which makes educational institutions innovative and student-centered reinforces both reach and retention. The comparative analysis demonstrates that AI-based print campaigns have better response rates and achieve higher rates of enrolment than traditional ones, and perception of the brand, in general. Also, the study supplements the theoretical models such as Technology Acceptance Model and Promotion of Innovations and shows that the use of AI in print advertising is based on the perceptions of usefulness, ease of use, and visible success. Despite some of the short-run limitations such as cost, experience and technological infrastructure, the long-run advantages are more than the short-run limitations.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Al-Kfairy, M., Mustafa, D., Kshetri, N., Insiew, M., and Alfandi, O. (2024). Ethical Challenges and Solutions of Generative AI: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Informatics, 11(3), Article 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11030058
Anvekar, S. V., Gurav, P. S., and Oza, K. S. (2025). Sales Forecasting Prediction Using Machine Learning. International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (IJEECS), 14(1), 15–19.
Argan, M., Dinç, H., Kaya, S., and Argan, M. T. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Advertising. ADCAIJ: Advances in Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence Journal. https://doi.org/10.14201/adcaij.28331
De Bruyn, A., Viswanathan, V., Beh, Y. S., Brock, J. K.-U., and von Wangenheim, F. (2020). Artificial Intelligence and Marketing: Pitfalls and Opportunities. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 51, 91–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intmar.2020.04.007
Enache, M. C. (2020). AI for Advertising. Annals of “Dunarea de Jos” University of Galati, Fascicle I: Economics and Applied Informatics, 26, 28–32. https://doi.org/10.35219/eai1584040978
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., Singh, R. P., and Suman, R. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications for Marketing: A Literature-Based Study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2022.08.005
Hatwar, L. R., Pohane, R. B., Bhoyar, S., and Padole, S. P. (2025). Mathematical Modeling on Decay of Radioactive Material Affects Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Research and Development in Management Review, 14(1), 180–182. https://doi.org/10.65521/ijrdmr.v14i1.501
Huh, J., Nelson, M. R., and Russell, C. A. (2023). ChatGPT, AI Advertising, and Advertising Research and Education. Journal of Advertising, 52(4), 477–482. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913367.2023.2227013
Järvi, K., Almpanopoulou, A., and Ritala, P. (2018). Organization of Knowledge Ecosystems: Prefigurative and Partial Forms. Research Policy, 47(8), 1523–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.05.007
Kandoth, S., and Shekhar, S. K. (2024). Scientometric Visualization of Data on Artificial Intelligence and Marketing: Analysis of Trends and Themes. Science Talks, 9, Article 100309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sctalk.2024.100309
Rahman, W. F. W. A., Che Fauzi, A. A., Wan Husain, W. S., Che Hassan, S. H., Nik Kamaruzaman, N. U. S., and Wan Abdul Aziz, W. N. H. (2020). The Usage of Artificial Intelligence in Marketing Automation: Potentials and Pitfalls. Journal of Mathematical and Computational Science, 6, 1–8.
Sorenson, O., and Fleming, L. (2020). Science as a Vocation: Knowledge Ecosystems and the Organization of Science. Research Policy, 49, Article 103994.
Stancu, A., and Panait, M. (2025). Marketing Strategy Metamorphosis Under the Impact of Artificial Intelligence Services. Systems, 13(4), Article 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040227
Verma, S., Sharma, R., Deb, S., and Maitra, D. (2021). Artificial Intelligence in Marketing: Systematic Review and Future Research Direction. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1, Article 100002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2020.100002
Vodă, A. I., Bortoș, S., and Şoitu, D. T. (2023). Knowledge ecosystem: A Sustainable Theoretical Approach. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 12(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.14207/ejsd.2023.v12n2p47
Wisetsri, W. (2021). Systematic Analysis and Future Research Directions in Artificial Intelligence for Marketing. Turkish Computer and Mathematics Education Journal, 12(11), 43–55. https://doi.org/10.17762/turcomat.v12i11.5825
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhKosh 2025. All Rights Reserved.

